Thermal Engineering
ADVERTISEMENT
mae 3309 – 002
THERMAL ENGINEERING
Solutions to HW # 2
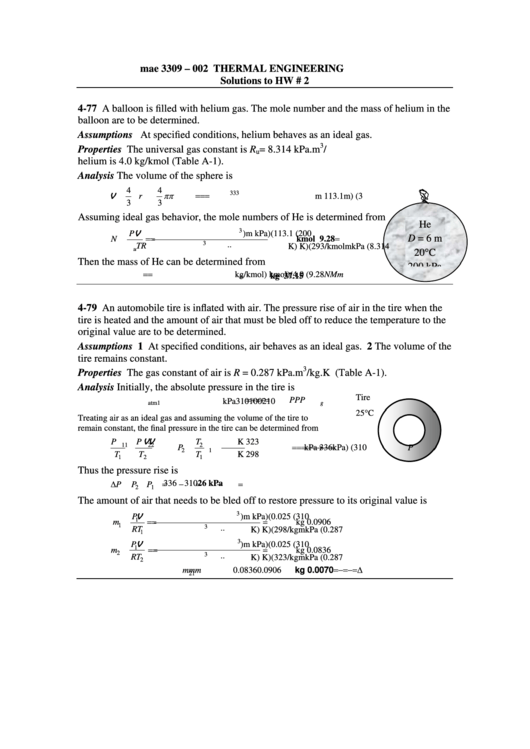
4-77 A balloon is filled with helium gas. The mole number and the mass of helium in the
balloon are to be determined.
Assumptions At specified conditions, helium behaves as an ideal gas.
3
Properties The universal gas constant is R
= 8.314 kPa.m
/kmol.K. The molar mass of
u
helium is 4.0 kg/kmol (Table A-1).
Analysis The volume of the sphere is
4
4
π
π
=
=
=
V
3
3
3
r
(3
m)
113.1
m
3
3
Assuming ideal gas behavior, the mole numbers of He is determined from
He
V
3
P
(200
kPa)(113.1
m
)
=
=
=
D = 6 m
N
9.28
kmol
⋅
⋅
3
R
T
(8.314
kPa
m
/kmol
K)(293
K)
u
20°C
Then the mass of He can be determined from
200 kPa
=
=
=
m
NM
(9.28
kmol)(4.0
kg/kmol)
37.15
kg
4-79 An automobile tire is inflated with air. The pressure rise of air in the tire when the
tire is heated and the amount of air that must be bled off to reduce the temperature to the
original value are to be determined.
Assumptions 1 At specified conditions, air behaves as an ideal gas. 2 The volume of the
tire remains constant.
3
Properties The gas constant of air is R = 0.287 kPa.m
/kg.K (Table A-1).
Analysis Initially, the absolute pressure in the tire is
Tire
=
+
=
+
=
P
P
P
210
100
310
kPa
1
g
atm
25°C
Treating air as an ideal gas and assuming the volume of the tire to
remain constant, the final pressure in the tire can be determined from
V
V
P
P
T
323
K
=
⎯
⎯→
=
=
=
1
1
2
2
2
P
P
(310
kPa)
336
kPa
2
1
T
T
T
298
K
1
2
1
Thus the pressure rise is
ΔP
=
−
=
−
=
P
P
336 310
26 kPa
2
1
The amount of air that needs to be bled off to restore pressure to its original value is
V
3
P
(310
kPa)(0.025
m
)
=
=
=
1
m
0.0906
kg
1
⋅
⋅
3
RT
(0.287
kPa
m
/kg
K)(298
K)
1
V
3
P
(310
kPa)(0.025
m
)
=
=
=
1
m
0.0836
kg
2
⋅
⋅
3
RT
(0.287
kPa
m
/kg
K)(323
K)
2
Δ
=
−
=
−
=
0.0070
kg
m
m
m
0.0906
0.0836
1
2
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4