Radicals, Trigonometric Ratio & Simplifying Square Roots Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
Page 4 of 4
Chapter Summary and Review continued
Examples on
10.5
S
C
R
INE AND
OSINE
ATIOS
pp. 563–565
EXAMPLE
Find sin A and cos A as fractions and as decimals.
B
leg opposite a A
2
0
≈ 0.6897
sin A
29
hypotenuse
2
9
20
leg adjacent to a A
2
1
≈ 0.7241
A
cos A
21
C
hypotenuse
2
9
Find sin A and cos A as fractions in simplest form and as decimals.
Round your answers to four decimal places if necessary.
46.
47.
48.
B
C
C
2 14
A
25
15
30 2
30 2
5
9
A
20
C
B
A
60
B
Approximate the value to four decimal places.
sin 57
sin 12
cos 31
cos 75
49.
50.
51.
52.
Find the lengths of the legs of the triangle. Round your
53.
10
x
answers to the nearest tenth.
31
y
Examples on
10.6
S
R
T
OLVING
IGHT
RIANGLES
pp. 569–571
Solve T XYZ.
EXAMPLE
74, so y ≈ 8.6.
2
2
2
By the Pythagorean Theorem, y
5
7
25
49
X
7
y
1.4 ≈ 54.5 .
1
tan X
1.4, so maX
tan
5
5
Since aX and aZ are complementary,
Y
7
Z
maX ≈ 90 – 54.5
maZ
90
35.5 .
aA is an acute angle. Use a calculator to approximate the measure of
aA to the nearest tenth of a degree.
tan A
3.2145
sin A
0.0888
cos A
0.2243
tan A
1.2067
54.
55.
56.
57.
Solve the right triangle. Round decimals to the nearest tenth.
q
58.
59.
60.
B
P
R
Y
x
Z
c
3
z
14
23
3
55
A
6
C
P
X
Chapter Summary and Review
579
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2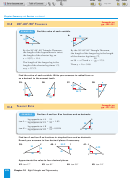 3
3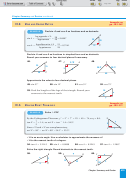 4
4