Rational Exponents - Math Worksheet
ADVERTISEMENT
MAP4C
1.3 Rational Exponents - Investigate!
1. Use a calculator to calculate each of the following and look for a pattern.
1
1
1
4
9
16
2
2
2
a)
= _______
b)
= _______
c)
= _______
1
1
1
25
36
49
2
2
2
d)
= _______
e)
= _______
f)
= _______
What is special about the bases? (4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49)
______________________________________________
2. Use a calculator to calculate each of the following.
4
9
16
a)
= _______
b)
= _______
c)
= _______
25
36
49
d)
= _______
e)
= _______
f)
= _______
1
a
2
How else could you write
? ______________
Taking the square root is the opposite operation to squaring (exponent 2). Therefore
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
a
a
2
2
2
2
2
and
1
1
1
1
1
2
2 2
2
3
2 2
3
4
2 2
4
5
2 2
5
a
2 2
a
3
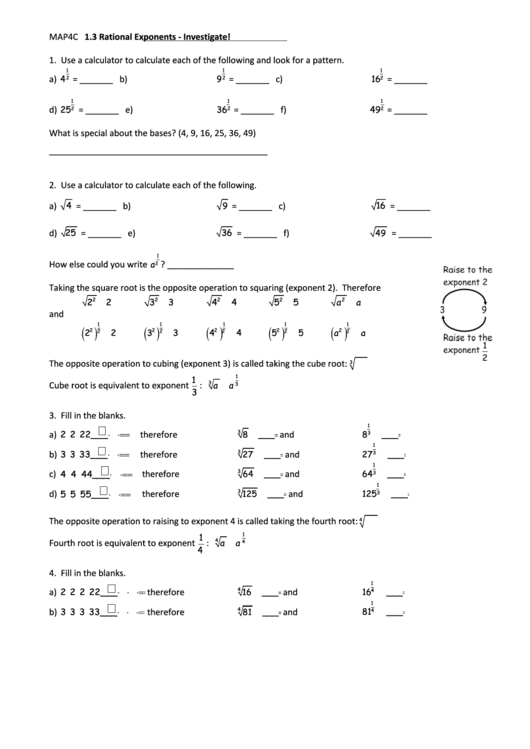
The opposite operation to cubing (exponent 3) is called taking the cube root:
1
1
3
a
a
3
Cube root is equivalent to exponent
:
3
3. Fill in the blanks.
1
2 2 2 2
___
3
8
___
8
___
3
a)
therefore
and
1
3 3 3 3
___
3
27
___
27
___
3
b)
therefore
and
1
4 4 4
4
___
3
64
___
64
___
3
c)
therefore
and
1
3
125
___
125
___
5 5 5 5
___
3
d)
therefore
and
4
The opposite operation to raising to exponent 4 is called taking the fourth root:
1
1
4
a
a
4
Fourth root is equivalent to exponent
:
4
4. Fill in the blanks.
1
2 2 2 2 2
___
4
16
___
16
___
4
a)
therefore
and
1
3 3 3 3 3
___
4
81
___
81
___
4
b)
therefore
and
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2








