Economic Formula Sheet - Descriptive Statistics
ADVERTISEMENT
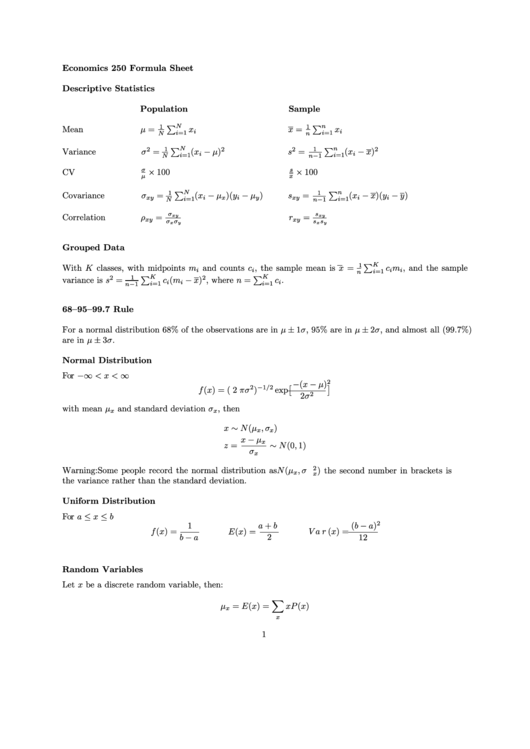
Economics 250 Formula Sheet
Descriptive Statistics
Population
Sample
1
1
N
n
Mean
μ =
x
x =
x
i
i
N
i=1
n
i=1
1
1
2
2
2
2
N
− μ)
n
− x)
Variance
σ
=
(x
s
=
(x
i
i
i=1
i=1
N
n−1
× 100
× 100
σ
s
CV
μ
x
1
1
N
− μ
− μ
n
− x)(y
− y)
Covariance
σ
=
(x
)(y
)
s
=
(x
xy
i
x
i
y
xy
i
i
i=1
i=1
N
n−1
σ
s
xy
xy
Correlation
ρ
=
r
=
xy
xy
σ
σ
s
s
x
y
x
y
Grouped Data
1
K
With K classes, with midpoints m
and counts c
, the sample mean is x =
c
m
, and the sample
i
i
i
i
n
i=1
2
1
2
K
K
− x)
variance is s
=
c
(m
, where n =
c
.
i
i
i
i=1
i=1
n−1
68–95–99.7 Rule
For a normal distribution 68% of the observations are in μ ± 1σ, 95% are in μ ± 2σ, and almost all (99.7%)
are in μ ± 3σ.
Normal Distribution
For −∞ < x < ∞
2
−(x − μ)
2
−1/2
f (x) = (2πσ
)
exp
2
2σ
with mean μ
and standard deviation σ
, then
x
x
x ∼ N (μ
, σ
)
x
x
x − μ
x
∼ N (0, 1)
z =
σ
x
2
) i.e. the second number in brackets is
Warning: Some people record the normal distribution as N (μ
, σ
x
x
the variance rather than the standard deviation.
Uniform Distribution
For a ≤ x ≤ b
2
(b − a)
1
a + b
f (x) =
E(x) =
V ar(x) =
b − a
2
12
Random Variables
Let x be a discrete random variable, then:
μ
= E(x) =
xP (x)
x
x
1
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4








