Soil Textural Triangle Worksheet
ADVERTISEMENT
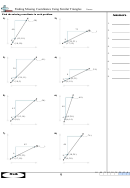
Soil Textural Triangle
Name: _________________________________________________ Period : _______ Date: _________
Essential Question: How do I classify the types of soil using the soil triangle?
A soil texture triangle is used to classify the texture class of a soil. The sides of the soil
texture triangle are scaled for the percentages of sand, silt, and clay.
Soil Texture is one of the first things
determined when a soil is examined. It is
related to weathering and rocks as parent
materials. The differences in horizons may be due to the
differences in texture of their respective parent materials
or rocks where soil formed.
First, look at the orientation of the percentages on the sides of the triangle. The numbers are arranged
symmetrically around the perimeter. On the left the numbers correspond to the percentage of clay, and
on the right the numbers correspond to the percentage of silt. At the bottom of the triangle chart are the
percentages of sand.
To classify a soil sample, you find the intersection of the
three lines that correspond the three proportions. On the
chart, all of the percents will add up to 100%.
Example: Classify a soil sample that is 30% clay, 15%
silt, and 55% sand. First locate 30% on the clay axis, and
draw a line horizontally from left to right. Next, locate 15%
on the silt axis, and draw a line going down diagonally to the
left. Finally, locate 55% on the sand axis, and draw a line
going up diagonally to the left. The intersection is in a region
called Sandy Clay Loam. See figure on the right.
In some environments clay aggregates form that are so strongly cemented together that they feel like fine
sand or silt. In humid climates iron oxide is the cement. Humid air can hasten the process of rusting, which an
example of chemical weathering.
Chemical weathering occurs when the minerals within the rocks are
chemically altered. Oxidation represents a form of chemical weathering where oxygen combines with
elements in the rock to form oxides. Iron-rich rocks provide a simple example of this: Oxidation results in
In desert climates silica is the cement and in arid
a rusting effect similar to the rust found on exposed iron.
regions lime can be the cement. It takes prolonged rubbing to show that they are clays and not silt
loams.Some soils derived from granite contain grains that resemble mica but are softer. Rubbing breaks down
these grains and reveals that they are clay. These grains resist dispersion and field and laboratory
determinations may disagree.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Life
 1
1 2
2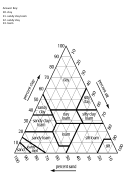 3
3