Passenger Medical Clearance Guidelines
Air travel has some unique features which must be considered by passengers with medical conditions and their treating
doctors to ensure a safe and comfortable flight.
The principle factors to consider when assessing a passenger’s fitness for air travel are:
•
Reduced atmospheric pressure: Cabin air pressure changes occur after take-off and before landing and lead to gas
expansion and contraction which may cause pain and pressure effects.
•
Reduction in oxygen tension: The aircraft cabin is pressurised to an equivalent of 6,000-8,000 feet and oxygen
partial pressure is approximately 20% less than on ground. Healthy passengers have no problems at these altitudes,
but passengers with anaemia or heart and lung conditions may be at risk and require supplemental oxygen during
air travel.
•
Inaccessibility to advanced medical care: The aircraft cabin is a closed environment where access to advanced
medical care may not be possible for several hours. Our cabin crew is trained in basic first aid and we do carry
medical kits and heart defibrillators on board, but advanced medical care onboard is not possible. If a passenger has
a medical condition that carry a high risk of requiring extraordinary medical assistance in flight they may not be
accepted for air travel.
Specific Medical Conditions
When calculating the number of days post-incident count the day of operation/onset of illness and day of travel.
Please note: The following is not an exhaustive list and the final decision regarding requirement for MEDA clearance will rest
with our in-house Aviation Medicine Specialists.
Diagnosis
Not fit to fly
Medical clearance required
Comments
Blood disorders
Anaemia
Hb < 7.5g/dl
Hb 7.5 – 10 g/dl
If acutely anaemic, Hb level should be assessed
more than 24 hours after last blood loss, which
must have ceased.
Sickle cell disease
< 10 days after
Within 10 days of sickling crisis
Accepted for travel 10 days after sickling crisis
Sickling crisis
if otherwise stable.
Cardiovascular and other Circulatory disorders
•
Angina
Unstable angina
Passengers with frequent chest pains
should consult their doctor regarding their
fitness to travel.
•
Must be stable and no angina at rest.
•
Have sufficient medications at hand to
relief an angina attack.
•
Myocardial infarction
Within 7 days
All 6 weeks post-MI
Any cardiac failure?
•
Any Arrhythmia?
•
Any post-MI angina pain?
•
Is the heart size larger than normal?
•
Any pre-attack angina?
If NO: Uncomplicated; may travel after 7 days.
If YES: Complicated. Disposition depends on
individual assessment (stability, success of
stenting, escort proposed, etc.)
•
Cardiac Failure
Uncontrolled heart
If require inflight oxygen.
Passengers with uncontrolled heart failure
failure
should consult their doctor regarding their
fitness to travel.
•
Adequate control is someone that can walk
50 meters (50yards) or go up a flight of
stairs on room air at a normal pace without
breathlessness. Otherwise, inflight oxygen
may need to be considered.
Reviewed: 22 August 2014
Page 2
 1
1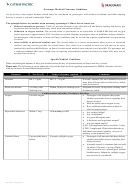 2
2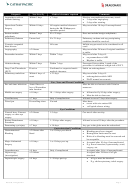 3
3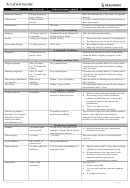 4
4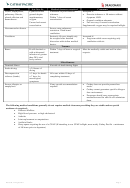 5
5 6
6 7
7








