Bikini Bottom: Blood Type Genetics And Codominance Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
If a person loses a lot of blood, he/she is given a blood transfusion: someone else’s blood is
injected into the person’s blood vessels. If you are given blood that does not match your blood
type, the antibodies in your blood will attack the antigens on the donated blood, causing the
donated red blood cells to burst or clump together and block blood vessels. Transfusion reactions
can be fatal, so doctors always test a person’s blood type before giving him/her donated blood.
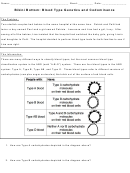
6. Test your understanding of blood groups by completing the table below.
Blood Group
Antigens on red
Antibodies in
Can receive
Can give blood
blood cells
blood
blood from
to
A
A
Anti-B
A and O
A and AB
B
B
AB
A and B
O
None
7. Based on the table above, which blood type would be considered a universal donor
(someone who can give blood to anyone)?
Your blood type is established before you are born by your genes, which were inherited from your
parents. You receive one allele for blood type from your mom and one allele for blood type from
your dad. The three possible alleles are:
A
I
: codes for A antigens on red blood cells
B
I
: codes for B antigens on red blood cells
i: does not code for any antigens
Everyone has TWO alleles for blood type in their cells, which means there are six possible
genotypes and four possible blood types.
8. List the six possible genotypes (combinations of alleles) for blood type. Group them
according to the four possible phenotypes (blood type).
Phenotype
Genotype
Type A (two genotypes possible)
Type B (two genotypes possible)
Type AB (one genotype possible)
Type O (one genotype possible)
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2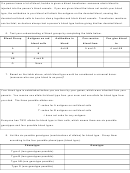 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6








