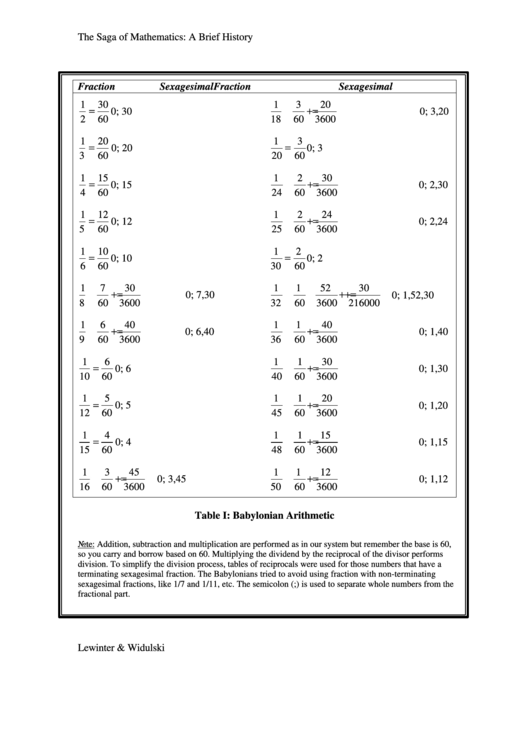
Table I: Babylonian Arithmetic
ADVERTISEMENT
The Saga of Mathematics: A Brief History
Fraction
Sexagesimal
Fraction
Sexagesimal
1
30
1
3
20
=
=
+
0; 30
0; 3,20
2
60
18
60
3600
1
20
1
3
=
=
0; 20
0; 3
3
60
20
60
1
15
1
2
30
=
=
+
0; 15
0; 2,30
4
60
24
60
3600
1
12
1
2
24
=
=
+
0; 12
0; 2,24
5
60
25
60
3600
1
10
1
2
=
=
0; 10
0; 2
6
60
30
60
1
7
30
1
1
52
30
=
+
=
+
+
0; 7,30
0; 1,52,30
8
60
3600
32
60
3600
216000
1
6
40
1
1
40
=
+
=
+
0; 6,40
0; 1,40
9
60
3600
36
60
3600
1
6
1
1
30
=
=
+
0; 6
0; 1,30
10
60
40
60
3600
1
5
1
1
20
=
=
+
0; 5
0; 1,20
12
60
45
60
3600
1
4
1
1
15
=
=
+
0; 4
0; 1,15
15
60
48
60
3600
1
3
45
1
1
12
=
+
=
+
0; 3,45
0; 1,12
16
60
3600
50
60
3600
Table I: Babylonian Arithmetic
Note: Addition, subtraction and multiplication are performed as in our system but remember the base is 60,
so you carry and borrow based on 60. Multiplying the dividend by the reciprocal of the divisor performs
division. To simplify the division process, tables of reciprocals were used for those numbers that have a
terminating sexagesimal fraction. The Babylonians tried to avoid using fraction with non-terminating
sexagesimal fractions, like 1/7 and 1/11, etc. The semicolon (;) is used to separate whole numbers from the
fractional part.
Lewinter & Widulski
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1