Solids, Liquids And Gases Worksheet With Answers Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
Interpreting Energy Changes during Heating, Cooling and Changes of State
Key Points:
1. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance.
2. When temperature is increasing, the motion of the particles in the substance is increasing.
3. When temperature is decreasing, the motion of the particles in the substance is decreasing.
4. The state of a substance determines the average potential energy of the particles in a substance.
5. In the solid state, the particles are very close together, so they have low potential energy.
6. In the liquid state, the particles are fairly close together, so they have medium potential energy.
7. In the gas state, the particles are very far apart, so they have very high potential energy.
When the temperature of a substance is changing, kinetic energy is changing and potential energy is
constant.
When the state of a substance is changing, potential energy is changing and kinetic energy is constant.
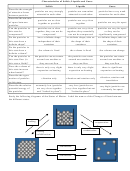
Cooling Curve for Pure Water
gas
condensing
100
liquid
freezing
0
solid
t
t
t
t
t
t
0
1
2
3
4
5
Time (min)
1. Refer to the cooling curve above, indicate if the following statements are True or False:
, the motion of the particles is decreasing. False. Temperature is not changing.
a) From t
to t
1
2
b) From t
to t
, the particles are getting closer together. False. State is not changing.
2
3
c) From t
to t
, the motion of the particles is decreasing. True. Temperature is decreasing.
0
1
d) From t
to t
, the potential energy of the particles is decreasing. True. The substance is turning solid.
3
4
e) From t
to t
, the motion of the particles is increasing. False. Motion is constant (temp is constant).
3
4
f) From t
to t
, the potential energy of the particles is constant. False. The substance is turning to liquid.
1
2
2. In regions on cooling curves when temperature is decreasing, what is happening to the:
a) motion of the particles: decreasing (decreasing temperature means that the particles are slowing
down, so the average motion of particles decreases)
b) distance between the particles: constant (state is not changing so particles are no closer together)
c) kinetic energy of the particles: decreasing (temperature measures average kinetic energy)
d) potential energy of the particles: constant (state is not changing so particles are no closer together)
e) state of the particles: constant (when state changes, the temperature is constant)
3. In regions on cooling curves when temperature is constant, what is happening to the:
a) motion of the particles: constant (temperature measures the motion of particles, and temp is constant)
b) distance between particles: decreasing (in regions where temp is constant, potential energy changes)
c) kinetic energy of the particles: constant (temperature measures the average kinetic energy of particles)
d) potential energy of the particles: decreasing as the particles get closer together and change state
e) state of the particles: changing (in regions where temp is constant, state is changing)
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6