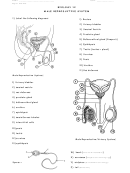
Biology School Worksheet Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
The F2 progeny, however, demonstrate Mendelian genetics. When the F1 roan individuals mate, the F2 progeny have
•
a phenotypic ratio of 1 red:2 roan:1 white.
This mode of inheritance is called incomplete dominance.
•
The phenotypic outcomes for cow color and incomplete dominance in general can be explained biochemically.
•
One allele of the gene codes for an enzyme that functions in the production of the red color. The other allele codes
•
for the gene to make white color. If both alleles are present, both are expressed, resulting in a cow that has some
red and some white.
Mendel's laws are not compromised here, he just happened to find in peas examples of complete dominance only.
•
•Not all alleles are dominant and recessive.
•Some alleles are equally strong and _______________ are ______________ by the other.
•Alleles which are equally strong are said to be "________________".
Codominance
•When _______________ alleles are present, they are _______________ expressed in the phenotype.
•The hybrid is a _______________ of both alleles.
•When expressing codominant alleles, both alleles are represented by different _______________ letters.
Complete the Punnet square for a cross between a black chicken (BB) and a white chicken (ww). Give the phenotype of the offspring?
C
B
C
B
-Black
W
W
C
C
-white
C
B
C
W
-checkered
What is the phenotype if the offspring?___________
What is the name of the inheritance pattern in which both alleles are expressed equally?
Blood Types and Codominance
In humans, there are four blood types (phenotypes): A, B, AB, and O
•
Blood type is controlled by three alleles. A, B, O
•
O is recessive, two O alleles must be present for the person to have type O blood
•
A and B are codominant. If a person receives an A allele and a B allele, their blood type is type AB
•
Crosses involving blood type often use an I to denote the alleles - see chart.
•
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6