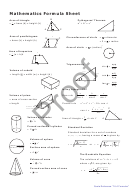
Mathematics Formula Sheet Page 8
ADVERTISEMENT
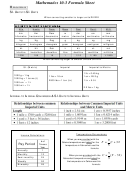
Probability & Statistics
Probability
∪
=
+
−
∩
P(
A
B
)
P(
A
)
P(
B
)
P(
A
B
)
∩
=
P(
A
B
)
P(
A
)
P(
B
|
A
)
P(
B
|
A
)
P(
A
)
=
P(
A
|
B
)
′
′
+
P(
B
|
A
)
P(
A
)
P(
B
|
A
)
P(
A
)
P(
A
)
P(
B
|
A
)
j
j
=
Bayes’ Theorem:
P(
A
|
B
)
j
Σ
P(
A
)
P(
B
|
A
)
i
i
Discrete distributions
For a discrete random variable X taking values
x with probabilities
p
i
i
μ
=
=
Σ
Expectation (mean):
E(
X
)
x
p
i
i
σ
2
μ
2
2
μ
2
=
=
Σ
−
=
Σ
−
Variance:
Var(
X
)
(
x
)
p
x
p
i
i
i
i
=
Σ
For a function
g(X :
)
E(g(
X
))
g(
x
)
p
i
i
Standard discrete distributions:
X =
P(
x
)
Distribution of X
Mean
Variance
np
np −
Binomial
B(
n
,
p
)
1 ( p
)
⎛
⎞
n
−
x
n
x
⎜ ⎜
⎟ ⎟
−
p
1 (
p
)
x
⎝
⎠
λ
λ
λ
Poisson
Po(
)
x
λ
λ
−
e
x
!
Continuous distributions
For a continuous random variable X having probability density function f
∫
μ
=
=
Expectation (mean):
E(
X
)
xf
(
x
d )
x
∫
∫
σ
μ
μ
=
2
=
−
2
=
2
−
2
Variance:
Var(
X
)
(
x
)
f(
x
d )
x
x
f
(
x
d )
x
∫
=
For a function
g( X :
)
E(g(
X
))
g(
x
)
f
(
x
d )
x
x
∫
=
≤
=
Cumulative distribution function:
F(
x
)
P(
X
x
)
f
(
t
d )
t
−
∞
Standard continuous distributions:
Distribution of X
P.D.F.
Mean
Variance
Uniform (Rectangular) on [a, b]
a +
1
1
2
(
b
)
1
b −
(
a
)
2
12
b −
U[a,b]
a
μ
μ
2
2
⎛ −
2
μ
σ
σ
x
Normal
N(
,
)
⎞
1
−
⎜
⎟
1
σ
⎝
⎠
2
e
σ
π
2
8
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10