Quadrilaterals Worksheet With Answers Page 41
ADVERTISEMENT
a) m∠DMA = 2x + 10
m∠CAB = x + 5
x = _______
m∠CAD =________
b) AB = (7x – 3) cm
DC = ( 5x + 9) cm
x = _________
AD = _________
2. The vertices of
ABCD are A(-2,-1), B(2,-3), C(4,1), and D(0,3).
a) Graph the parallelogram in the coordinate plane.
b) Identify the parallelogram as a rectangle, square, or rhombus.
c) Justify this answer.
Solutions:
DB ⊥
(The diagonals of a square are ⊥.)
1. a)
AC
m∠DMA = 90
(⊥s form right angles.)
2x + 10 = 90
(Substitution)
2x = 80
(Addition/subtraction property of equality)
x = 40
(Division/multiplication property of equality)
m∠CAD + m∠CAB = m∠DAB (Angle addition property)
m∠CAD = m∠CAB
(A diagonal bisects a pair of opposite angles
in a square.)
m∠DAB = 90
(Definition of a square)
m∠CAD + m∠CAD = 90
(Substitution)
2 m∠CAD = 90
m∠CAD = 45
(Division/multiplication property of equality)
(Opposite sides of a square ≅ and have =
b) AB = DC
measures.)
7x-3=5x+9
(Substitution)
2x = 12
x = 6
(Division/multiplication property of
equality)
AD = AB
(Definition of a square)
AD = 7•6 – 3 = 42-3 = 39 cm
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2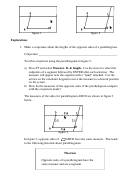 3
3 4
4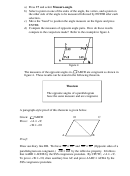 5
5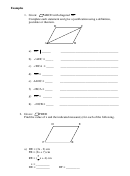 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9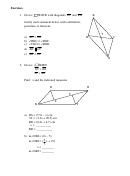 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18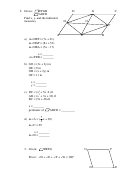 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27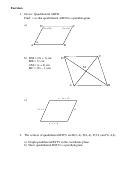 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31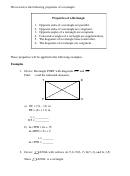 32
32 33
33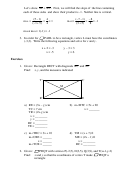 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50