Quadratic Equations Worksheet With Answers
ADVERTISEMENT
3.2 – Quadratic Equations
nd
2
Quadratic (2
degree) equations take the standard form;
Ax
+ Bx + C = 0
Three possible solutions exit when trying to solve these equations. One can check the
=
−
2
discriminant,
d
b
4
ac
, to determine the number of solutions but these are best shown
graphically as outlined below.
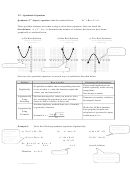
a) No Real Solution
b) One Real Solution
c) Two Real Solutions
(Complex solutions?)
(or two equal solutions)
(or two distinct solutions)
2
2
2
(b
-4ac<0)
(b
-4ac=0)
(b
-4ac>0)
Crosses x-axis
at two points
Does not cross x-axis
Touch x-axis at one point
One can solve quadratic equations in several ways as outlined in the table below.
Method
How it works
Advantages/Disadvantages
Great visual method proves
Graph then examine the corresponding function
useful especially when solving
Graphically
to see at what x- value the function equals the
inequalities.
values you are interested in.
Not always accurate
Algebraically
Set function equal to value you want to solve
Generates accurately solutions
Using
for, rearrange the equation to zero, and then
for integral factors
Factoring
factor to find x-value(s) if they exits
Another algebraic method than uses a formula
Works for all Real numbers
to generate solutions.
Algebraically
Can program formula into
Using
calculator so just need to enter
−
±
−
2
Formula
b
b
4
ac
=
coefficients a, b, c
Formula is
x
2
a
Example 1:
Solve the following quadratic equations algebraically
Rearrange in
descending order
2
2
2
Zero Principle
a) 0 = x
+ 5x – 36
b)
x
– 6x = -9
c) 4x = 3x
+ 8
one of the
multipliers must
2
2
0 = (x + 9) (x – 4)
x
– 6x + 9 = 0
0 = 3x
- 4x + 8
be zero to give
2
(x - 3)
= 0
zero result
So
0 = x + 9 or 0 = x - 4
-9 = x
4 = x
x = 3
no real solution
Therefore x = -9, 4
One solution
Discriminant provides
quick check for the nature
2
of the roots. (b
-4ac<0)
3.2 – quadratic equations
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2








