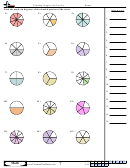
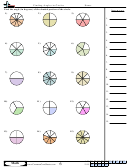
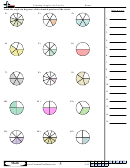
Energy Flow In Ecosystems - Biology Worksheet With Answers Page 14
ADVERTISEMENT
11. According to the laws of conservation of matter and energy, neither matter nor energy can be created or
destroyed. They can only change forms.
Although it is true that only 10% of the energy that is available at one trophic level is transferred to the next
level, the rest changes into heat energy, so the total amount of energy is still conserved. However, the heat
energy is considered "lost" because it is not useful to the system.
Likewise, even though only a portion of matter is transferred from trophic level to trophic level, the remaining
"waste" is recycled through processes such as the carbon or nitrogen cycles. Thus, the total amount of matter
is also conserved.
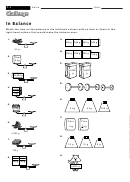
12. In most ecosystems, energy does not follow simple straight paths because individual animals often feed at
several trophic levels. This creates a complicated, interconnected group of food chains called a food web.
13. --
14. Food webs provide visual representations that identify the relationships among producers, consumers,
and decomposers carrying out either autotrophic or heterotrophic nutrition. In a food web, arrows are drawn
between organisms to show the directions in which food energy is transferred.
15. Although plants and other producers make up the first trophic level of all food webs or food chains, the
ultimate source of energy for all ecosystems is the Sun. A continuous input of energy from the Sun drives
many natural processes found in all ecosystems such as photosynthesis and the water cycle.
16. A food web shows the connections between the living things in an environment. An arrow from one living
thing to another indicates that the living thing is a source of energy for the living thing that the arrow is pointing
to. In this case, the food web shows that squirrels are a source of energy for both foxes and owls.
17. The law of conservation of energy is universal. Energy cannot be created nor destroyed. There is less
energy available in the top of the energy pyramid than there is in the bottom because organisms all along the
energy pyramid are using the energy, and some of the energy is lost between each trophic level as heat.
The heat energy is dispersed into the surrounding environment.
18. --
19. As energy flows through ecosystems, atoms and molecules cycle among both the living and nonliving
components of the biosphere.
The atoms and molecules on Earth cycle among organisms as well as the nonliving components of the
biosphere, such as atmospheric gases. For example, atoms in carbon dioxide and water molecules that are
used in photosynthesis to form energy-rich organic compounds are returned to the environment when cells
break these compounds down to release the energy.
20. The energy in a food chain initially enters through the green plants at the beginning of the chain. The plants
make food from the energy they absorb from the Sun.
21. As energy travels from one trophic level up to the next in an energy pyramid, there is a great amount of
energy lost. An average of only 10% of the energy from the previous level moves to the next level. The rest is
used up or lost as heat energy.
22. Ecologists often illustrate the flow of energy through ecosystems with an energy pyramid, a diagram in
which trophic levels are represented by stacked blocks. The size of each block is determined by the amount of
energy stored in the organisms at that trophic level.
23. --
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15