2.1-2.5, 3.1-3.4 Exam 2 Review Math Worksheet With Answers Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
3
2.4: Graphing Techniques
Memorize rules for determining symmetry
– A graph has y-axis symmetry if replacing x with -x results in an equivalent equation
– A graph has x-axis symmetry if replacing y with -y results in an equivalent equation
– A graph has origin symmetry if replacing both x with -x and y with -y results in an equivalent
equation
Be familiar with common restrictions:
anything
– Avoid
and
negative
0
Look at resulting values in common graphs:
–
positive
0
2
–
(anything)
0
–
anything
0
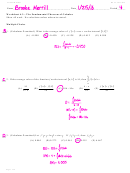
9. Graph y =
2 x
3 + 1.
Solution:
No symmetry
5
7
x intercepts at (
, 0) and (
, 0), y intercept at (0, 5)
2
2
No restrictions on x. y
1
The graph of y = x is shifted reflected across the x-axis and becomes twice as narrow. Then it
is shifted 1 unit up and 3 units right.
2
10. Graph y =
x
+ x
2.
Solution:
No symmetry
x intercepts at ( 2, 0) and (1, 0), no y intercept
x
2 or x
1 and y
0
You have to plot points since there isn’t really a basic graph we’re working with here.
x + 1
11. Graph y =
.
2
x
+ x
6
Solution:
No symmetry
1
x intercept at ( 1, 0), y-intercept at 0,
6
Restrictions are x = 2 and x =
3.
You have to plot points since there isn’t really a basic graph we’re working with here.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7