Quadratic Functions Worksheets With Answers
ADVERTISEMENT
Pre-Calculus 11
Name:__________________
Ch. 3 Quadratic Functions.
Lesson Notes 3.3
:
Completing the Square
Objectives:
•
converting quadratic functions from standard to vertex form
•
analysing quadratic functions of the form y = ax
2
+ bx + c
•
writing quadratic functions to model situations
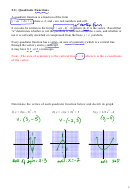
Up till now, you have learned how to express a quadratic function in standard form,
f (x) = ax
2
+ bx + c, or in vertex form, f (x) = a(x – p)
2
+
You can determine the shape of the graph
q.
and direction of opening from the value of
in either form. The vertex form has the
advantage
that
a
you can identify the coordinates of the vertex as
(p,
q) directly from the algebraic form. It is useful to
be able to determine the coordinates of the vertex algebraically when using quadratic functions to
model problem situations involving
and
values.
maximum
minimum
Today, we will go over the way of converting a quadratic function in standard form to
vertex form using an algebraic process called
completing the
square. Completing the square involves
adding a value to and subtracting a value from a quadratic polynomial so that it contains a perfect
square trinomial. You can then rewrite this trinomial as the square of a binomial.
Do you remember this?
a) (x + 3)
2
=
b) (x – 3)
2
=
c) (x + 13)
2
=
d) (x – 8)
2
=
2
e) (x +
)
2
=
3
5
2
f) (x –
)
=
9
g) (x + m)
2
=
h) (x – 2k)
2
=
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5