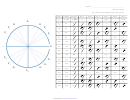
Circles And Circular Functions Worksheet - Dr. Neal, Math 116 - 2008 Page 5
ADVERTISEMENT
Dr. Neal, Fall 2008
Solutions
5
25
2
2
1. Using r =
+ y
=
, the equation becomes x
.
3
9
2
4 × 6
1
1
25
25
1
24
24
2 6
2
2
For x = −
, then −
+ y
=
→ y
=
−
=
→ y = ±
= ±
= ±
3
3
9
9
9
9
9
3
3
1
2 6
.
So the points on the circle are −
, ±
3
3
2
2
+ y
= 9; so the upper semicircle
2
(c) To solve y = 2, we have
9 − x
= 2 ,
2.
x
2
2
2
function is y = 9 − x
for −3 ≤ x ≤ 3. The
or 9 − x
= 4 . So x
= 5 and x = ± 5 .
range for y is [0, 3].
(d) y ≥ 2 for − 5 ≤ x ≤ 5 ,
and y < 2 for x in [–3, − 5 ) or in ( 5, 3].
− 5
5
2
2
+ y
= 49 ; so the lower semicircle is
2
(c) To solve y = −3, use − 49 − x
= −3,
3. x
2
2
2
y = − 49 − x
, for −7 ≤ x ≤ 7. The range
49 − x
= 9 .
= 40
or
Then
and
x
x = ± 40 = ± 2 10 .
for y is [–7, 0].
(d) y < −3 for − 40 < x < 40 ,
and y ≥ −3
for x in [–7, − 40 ] or in [ 40, 7].
2
2
2
4 (a) Use (x − h)
+ (y − k )
= r
.
(8, 2)
2
2
Here (x − 8)
+ (y + 2)
= 16.
2
2
(c) (y + 2)
= 16 − (x − 8)
; so
(4, -2)
(8, -2)
(12, -2)
2
y = 16 − (x − 8)
− 2 , for 4 ≤ x ≤ 12 .
The range for the
(8, -6)
upper-semicircle function is −2 ≤ y ≤ 2.
2
(d) y = − 16 − (x − 8)
− 2 for 4 ≤ x ≤ 12 with range −6 ≤ y ≤ −2 .
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4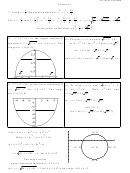 5
5