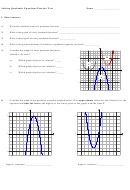
Algebra 3 Solving Quadratic Equations Worksheet - Brunel University Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
Case 1.
Two distinct, real roots, the vertex lies on the opposite side of the
x-axis from the rest of the graph and so the curve must cross the
x-axis exactly twice. One can see from the graph where the roots
are, and they are clearly real numbers.
Analytically, this corresponds to the case when the
discriminant
D > 0
of the quadratic equation is
strictly positive
(
) .
6
5
4
2
f (x) = 3x
9x + 6
3
f x
a > 0
2
1
D > 0
0
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
x
20
15
2
f (x) =
3x
9x+10
10
f x
a < 0
5
D > 0
.
0
6
4
2
0
2
x
4
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2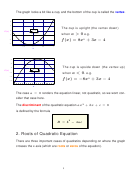 3
3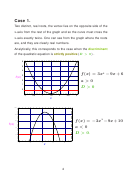 4
4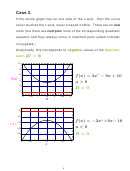 5
5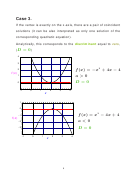 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13