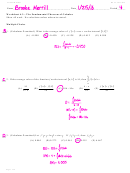
Ap Statistics Solutions To Packet 6 - Probability The Study Of Randomness Worksheet With Answers Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
6.11 DESCRIBE THE SAMPLE SPACE In each of the following situations, describe a sample
space S for the random phenomenon. In some cases you have some freedom in specifying S,
especially in setting the largest and the smallest value in S.
(a) A seed is planted in the ground. It either germinates or fails to grow.
S = {germinates, fails to grow}.
(b) A patient with a usually fatal form of cancer is given a new treatment. The response variable is the
length of time that the patient lives after treatment.
If measured in weeks, for example, S = {0, 1, 2, . . .}.
(c) A student enrolls in a statistics course and at the end of the semester receives a letter grade.
S = {A, B, C, D, F}.
(d) A basketball player shoots four free throws. You record the sequence of hits and misses.
Using Y for “yes (shot made)” and N for “no (shot missed),” S = {YYYY, NNNN, YYYN,
NNNY, YYNY, NNYN, YNYY, NYNN, NYYY, YNNN, YYNN, NNYY, YNYN, NYNY,
YNNY, NYYN}. (There are 16 items in the sample space.)
(e) A basketball player shoots four free throws. You record the number of baskets she makes.
S = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4}.
6.14 LISTING OUTCOMES, I For each of the following, use a tree diagram or the multiplication
principle to determine the number of outcomes in the sample space.
(a) Toss 2 coins.
If two coins are tossed, then by the multiplication principle, there are (2)(2) = 4
possible outcomes. The outcomes are illustrated in the following tree diagram: The sample
space is {HH, HT, TH, TT}.
(b) Toss 3 coins.
If three coins are tossed, then there are (2)(2)(2) = 8 possible outcomes. The
outcomes are illustrated in the following tree diagram: The sample space is {HHH, HHT,
HTH, HTT, THH, THT, TTH, TTT}.
3
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2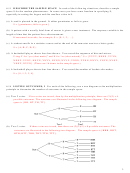 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21