Chemical Bonds Chart
ADVERTISEMENT
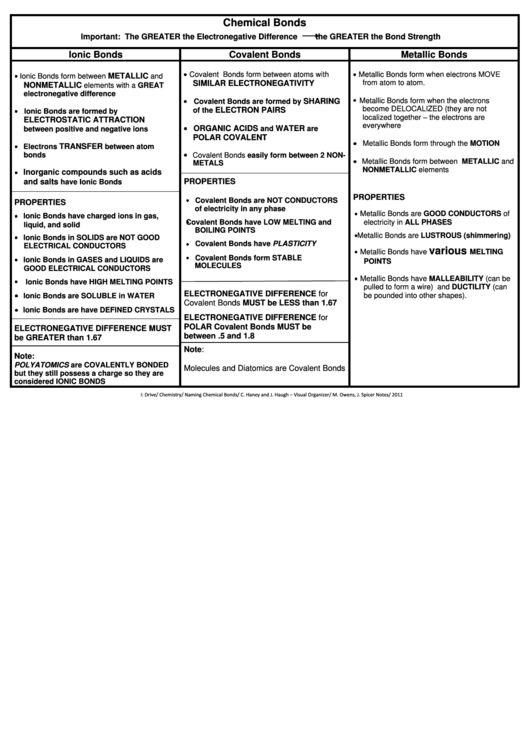
Chemical Bonds
Important: The GREATER the Electronegative Difference
the GREATER the Bond Strength
Ionic Bonds
Covalent Bonds
Metallic Bonds
Covalent Bonds form between atoms with
Metallic Bonds form when electrons MOVE
METALLIC
Ionic Bonds form between
and
SIMILAR ELECTRONEGATIVITY
from atom to atom.
NONMETALLIC
elements with a GREAT
electronegative difference
Metallic Bonds form when the electrons
SHARING
Covalent Bonds are formed by
become DELOCALIZED (they are not
of the
ELECTRON PAIRS
Ionic Bonds are formed by
localized together – the electrons are
ELECTROSTATIC ATTRACTION
everywhere
ORGANIC ACIDS
WATER
and
are
between positive and negative ions
POLAR COVALENT
Metallic Bonds form through the MOTION
TRANSFER
Electrons
between atom
bonds
Covalent Bonds easily form between 2 NON-
Metallic Bonds form between METALLIC and
METALS
NONMETALLIC elements
Inorganic compounds such as acids
and salts
have Ionic Bonds
PROPERTIES
PROPERTIES
Covalent Bonds are NOT CONDUCTORS
PROPERTIES
of electricity in any phase
Metallic Bonds are GOOD CONDUCTORS of
Ionic Bonds have charged ions in gas,
electricity in ALL PHASES
Covalent Bonds have LOW MELTING and
liquid, and solid
BOILING POINTS
Metallic Bonds are LUSTROUS (shimmering)
Ionic Bonds in SOLIDS are NOT GOOD
Covalent Bonds have PLASTICITY
ELECTRICAL CONDUCTORS
various
Metallic Bonds have
MELTING
Covalent Bonds form STABLE
Ionic Bonds in GASES and LIQUIDS are
POINTS
MOLECULES
GOOD ELECTRICAL CONDUCTORS
Metallic Bonds have MALLEABILITY (can be
Ionic Bonds have HIGH MELTING POINTS
pulled to form a wire) and DUCTILITY (can
ELECTRONEGATIVE DIFFERENCE for
be pounded into other shapes).
Ionic Bonds are SOLUBLE in WATER
Covalent Bonds MUST be LESS than 1.67
Ionic Bonds are have DEFINED CRYSTALS
ELECTRONEGATIVE DIFFERENCE for
POLAR Covalent Bonds MUST be
ELECTRONEGATIVE DIFFERENCE MUST
between .5 and 1.8
be GREATER than 1.67
Note:
Note:
POLYATOMICS are COVALENTLY BONDED
Molecules and Diatomics are Covalent Bonds
but they still possess a charge so they are
considered IONIC BONDS
I: Drive/ Chemistry/ Naming Chemical Bonds/ C. Haney and J. Haugh – Visual Organizer/ M. Owens, J. Spicer Notes/ 2011
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1