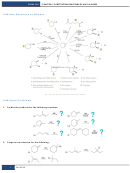
Reaction Map: Reactions Of Alkanes, Alkyl Halides, Alkenes, Alkynes And Alcohols Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
Oxidative cleavage with
KMnO
, acid,
cleaves C=C to give two carbonyls. Alkenyl
31
NaH (strong
56
Formation of epoxides from
Internal S
2 reaction: inversion of
4
N
heat
C-H bonds oxidized to C–OH
KMnO
base)
halohydrins
configuration at carbon
4
32
Cyclopropanation (Simmons-
Cu/Zn, CH
I
syn-selective
2
2
+
H
O
(or
Protonation of epoxide, then attack of H
O at
57
Opening of epoxides with
3
2
Smith)
aqueous acid
H
O/H
SO
)
most substituted carbon
2
2
4
33
Dichlorocyclopropanation
CHCl
, KOH
syn-selective
3
H
SO
, heat
Follows Zaitsev's rule (most sub. alkene
58
Elimination of alcohols to
2
4
formed). Rearrangements can occur
form alkenes (acidic)
34
Acid-catalyzed ether
H
SO
, ROH
Markovnikov selective, rearr. possible
2
4
formation
POCl
,
E2 reaction
59
POCl
elimination of
3
3
Hg(OAc)
, ROH,
pyridine
Markovnikov selective, alcohol is solvent
alcohols to alkenes
35
Oxymercuration
2
then NaBH
4
HI, heat
Can proceed through S
2 or S
1 depending
Hg(OAc)
, H
O,
60
Acidic cleavage of ethers
Oxymercuration
Markovnikov selective, water is solvent
36
N
N
2
2
on type of alcohol
then NaBH
4
BH
, then NaOH,
anti-Markovnikov selective, syn-selective
37
Hydroboration
PBr
61
Conversion of alcohols to
S
2 reaction. PCl
can also be used to make
3
3
N
3
H
O
alkyl chlorides
2
2
alkyl halides with PBr
3
H
SO
, H
O
Markovnikov selective; rearr possible
38
Acid-catalyzed hydration
2
4
2
SOCl
Usually taught as S
2. Pyridine can be used
62
SOCl
conversion of
2
+
2
N
("H
O
")
3
as base.
alcohols to alkyl chlorides
Lindlar, H
syn-selective
39
Partial hydrogenation
2
HCl, HBr, HI
Can go through S
1 or S
2 depending on
63
Alcohols to alkyl halides
(Lindlar)
N
N
with HX
type of alcohol
Na/NH
anti-selective
40
Partial hydrogenation
3
(sodium reduction)
TsCl or MsCl
Does not affect stereochemistry. Can use a
64
Tosylate and mesylate
BH
, then NaOH,
Alkyne hydroboration
anti-Markovnikov selective; tautomerization
41
formation
base such as pyridine.
3
H
O
2
2
I
(oxidant)
HgSO
, H
O,
65
Disulfide formation
Can use other oxidants but I
is most
Markovnikov selective; tautomerization
42
Alkyne Oxymercuration
2
4
2
2
common
H
SO
2
4
PCC
1° alcohols to aldehydes; 2° alcohols to
O
66
Alcohol oxidation with PCC
Carboxylic acids formed; terminal alkynes
43
Alkyne Ozonolysis
3
ketones
give CO
2
K
Cr
O
+
1° alcohols to carboxylic acids, 2° alcohols
67
Alcohol oxidation with
2
2
7
KMnO
, H
+
same as ozonolysis
44
Alkyne Ox. Cleavage
4
acid
to ketones.
H
CrO
2
4
[KMnO
4]
Dess Martin
68
Dess Martin oxidation
1° alcohols to aldehydes; 2° alcohols to
Pd/C, H
Hydrogenation
Adds twice to alkynes
45
2
Periodinane
ketones
Grignards,
Cl
, Br
, or I
Each individual reaction is anti-selective
69
Basic ring opening of
Add to least substituted position of epoxides
46
Alkyne double halogenation
2
2
2
–
(2 equiv)
epoxides
OH, LiAlH
4
Cl
, Br
, or I
anti-selective
47
Halogenation
2
2
2
(1 equiv)
H–Cl
Markovnikov selective
48
Addition of H–Cl to Alkynes
H–Br
49
Addition of H–Br to Alkynes
Markovnikov selective
H–I
Markovnikov selective
50
Addition of H–I to Alkynes
H–Cl, H–Br,
Addition of H–X to
Markovnikov selective
51
or H–I
haloalkenes
H–Cl [2 equiv]
Adds twice to alkyne; Markovnikov selective
52
Double addition of H–Cl to
Alkynes
H–Br [2 equiv]
53
Double addition of H–Br to
Adds twice to alkyne; Markovnikov selective
Alkynes
H–I [2 equiv]
Double addition of H–I to
Adds twice to alkyne; Markovnikov selective
54
Alkynes
NaNH
[2
vicinal or geminal dihalides; for terminal
55
Elimination of dihalides to
2
equiv]
give alkynes
alkynes, 3 equiv NaNH
required
2
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2