Water Quality Mathematical Expressions & Relationships Reference Sheet Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
Let's look at an example calculation for water containing 35 mg Ca/L and 22 mg Mg/L.
Calculation of Calcium Carbonate Hardness
Data:
Analyte
mg/L
mg/meq
meq/L
Calcium
35
20.04
1.75
Magnesium
22
12.16
1.81
CaCO
----
50.05
----
3
To Calculate hardness as mg CaCO
/L:
3
meq/L = (mg/L) / (mg/meq)
Hardness mg/L = [(meq Ca/L) + (meq Mg/L)] x [50.05]
Substituting the data from above table,
Hardness as mg CaCO
/L = (1.75 + 1.81)(50.05) = 178 mg/L
3
Now let's convert this result to grains/gallon,
Hardness in gr/gal = (178 mg/L) / (17.1 mg/gr) = 10.4 gr/gsl
The following table is provided for easy reference and lists the major cations and anions
found in most natural water. Listed for each analyte are its valence, millimolecular
weight (mg/mMole) and milliequivalent weight (mg/meq).
Cations
Valance
mMolar wt
meg wt
Calcium
+ 2
40.08
20.04
Magnesium
+ 2
24.32
12.16
Sodium
+ 1
22.99
22.99
Potassium
+ 1
39.10
39.10
Anions
Valance
mMolar wt
meq wt
Carbonate
-
2
60.01
30.01
Bicarbonate
-
1
61.02
61.02
Chloride
-
1
35.46
35.46
Fluoride
-
1
19.00
19.00
Nitrate as N
-
1
14.01
14.01
Nitrite as N
-
1
14.01
14.01
Sulfate
-
2
96.06
48.03
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Life
 1
1 2
2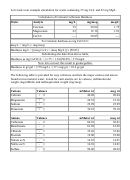 3
3








