The Mental Status Examination Chart Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
2
Glasgow Coma Scale
CATEGORY
SCORE
Eyes open (E)
Major Components of the Mental Status Examination
Spontaneously
4
Appearance
Age, sex, race, body build, posture, eye
contact, dress, grooming, manner,
To speech
3
attentiveness to examiner, distinguishing
features, prominent physical abnormalities,
To pain
2
emotional facial expression, alertness
None
1
Retardation, agitation, abnormal
Motor
Best motor response (M)
movements, gait, catatonia
Obeys command
5
Rate, rhythm, volume, amount,
Speech
articulation, spontaneity
Localizes pain
4
Affect
Stability, range, appropriateness, intensity,
Flexion to pain
3
affect, mood
Extension to pain
2
Suicidal ideation, death wishes, homicidal
Thought
content
ideation, depressive cognitions, obsessions,
None
1
ruminations, phobias, ideas of reference,
Best verbal response (V)
paranoid ideation, magical ideation,
delusions, overvalued ideas
Oriented
5
Associations, coherence, logic, stream,
Thought
Confused
4
clang associations, perseveration,
process
neologism, blocking, attention
Inappropriate words
3
Perception
Hallucinations, illusions,
Incomprehensible sounds
2
depersonalization, derealization, déjà vu,
None
1
jamais vu
Summed coma scale = E + M + V
Intellect
Global impression: average, above
average, below average
Insight
Awareness of illness
6. Are there short forms of the MSE?
Adapted from Zimmerman M: Interviewing Guide for
Evaluating DSM-IV Psychiatric Disorders and the Mental
Several shortened forms of the MSE have been developed as
Status Examination. Philadelphia, Psychiatric Press
screening instruments. All are composed of a combination of
Products, 1994, pp 121–122.
measures to detect cognitive impairments more accurately.
Although helpful, such exams must be combined with
clinical history. The diagnosis of dementia and delirium also
requires the demonstration of a decline in cognitive
5. What is the first step in the MSE?
functioning from a higher baseline. All screening exams have
difficulty in identifying patients with mild cognitive
A determination of consciousness must be the first step in
impairment and patients with focal neurologic lesions, such
MSE. Basic brain function determines the patient’s ability to
as subdural hematomas or meningiomas. The key point is
relate to the surroundings and cooperate with the interviewer.
that MSEs should not be used as the sole criteria for
Disturbance of this basic function affects higher level mental
diagnosing delirium or dementia.
processes that make up the major portions of the exam. The
Glasgow Coma Scale was developed by Teasdale and Jennett
7. What are some of the more common screening exams?
in 1974 to assess impaired consciousness. It is based on eye
opening and motor and verbal responses to stimuli. The scale
ranges from 3 (deep coma) to 14 (full-alert wakefulness).
The Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) is probably the
best known. The MMSE tests orientation, immediate and
short-term memory, concentration, arithmetic ability,
language, and praxis. It takes about 10 minutes to administer.
The Cognitive Capacity Screening Examination (CCSE) tests
orientation, serial subtraction, memory, and similarities. It is
less sensitive to delirium or dementia in the elderly. The
Neurobehavioral Cognitive Status Examination (NCSE) is
especially good for medically ill patients; it focuses on
consciousness, orientation, attention, language, construction,
memory, calculations, and reasoning. It tends to be more
sensitive in detecting impairment because it is more detailed.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Medical
 1
1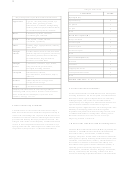 2
2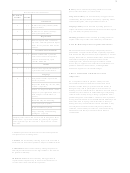 3
3 4
4








