Carson Elementary And Intermediate Algebra 3e
ADVERTISEMENT
M098
Carson Elementary and Intermediate Algebra 3e
Section 7.6
Objectives
1.
Solve equations containing rational expressions.
Vocabulary
Extraneous
An apparent solution that does not solve its equation.
solution
Prior Knowledge
1. Difference between equations and expressions.
It is important to remember the difference between expressions and equations. Expressions can be
simplified but they can not be solved. Equations, on the other hand, can be solved.
2. Solve linear equations with fractions.
7
x
x
5
1
12
8
4
Clear the fractions by multiplying each term by the LCD,
7
x
x
5
1
24
24
24
which is 24.
12
8
4
2(7x) – 3(x – 5) = 6(1)
Reduce each term.
14x – 3x + 15 = 6
Remove parentheses by multiplying and using the
distributive property. Be careful to distribute the minus
to BOTH terms in the parentheses.
11x + 15 = 6
Combine like terms
11x = -9
Subtract 15 from both sides.
Divide both sides by 11.
9
x
11
New Concepts
1. Solve equations containing rational expressions.
We spent quite a little time in Chapter 2 working with equations that contained fractions. Solving a
rational equation with a variable in the denominator is solved the same way with the addition of one
step. We must keep in mind that the denominator can not be equal to zero. As soon as you determine
the LCD, indicate the restrictions that must be placed on your results; those numbers that will cause
the denominator to equal zero. If one of these numbers should be one of the solutions when you solve
the equation, it must be eliminated. These are referred to as extraneous solutions.
3
2
7
x
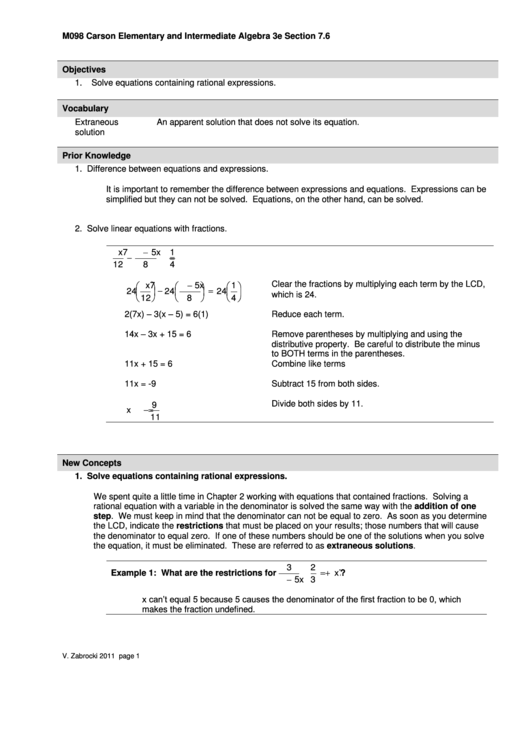
Example 1: What are the restrictions for
?
x
5
3
x can’t equal 5 because 5 causes the denominator of the first fraction to be 0, which
makes the fraction undefined.
V. Zabrocki 2011
page 1
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3








