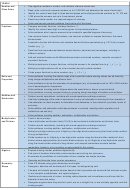
Maths Statutory Expectations Year 1 To Year 6 Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
DIVISION
STATUTORY EXPECTATIONS
Rapid Recall/Mental Calculations
Non-statutory guidance
Children … solve
Pictures/Objects
Symbolic
Practical / recorded
There are 8 raisins.
problems, including
using ICT (eg digital
Take half of them.
6 cakes shared between 2
6 cakes shared between 2
doubling, halving and
photos/pictures on IWB)
How many do you have?
sharing. [Expected]
Share the 10 grapes
They solve practical
between 2 people.
problems that involve
YR
6 cakes put into groups of 2
sharing into equal
6 cakes put into groups of 2
groups. [Exceeding]
Solve one-step problems
Practical/recorded using ICT
Pictures/Symbolic
Visual (modelled using bead strings)
Recognise/find/name ½ as one of
Find simple fractions of objects,
using concrete objects,
two equal parts of an object, shape
There are 14 people on the
How many apples in each bowl if I share 12 apples
numbers and quantities
15 ÷ 5 = 3
pictorial representations
or quantity.
bus. Half of them get off.
between 3 bowls?
and arrays (with the
Recognise/find/name ¼ as one of
Count on/back in 2s, 5s and 10s
How many remain on the bus?
four equal parts of an object, shape
Y1
support of the teacher)
There are 20 people in the
or quantity.
0
5
10
15
class. One quarter are boys.
How many boys are there?
Begin to use other multiplication
Calculate statements
Pictures/Symbolic
Visual
Arrays
Partitioning
Recall & use division facts for the 2,
Pupils use a
tables/recall facts, including
within the multiplication
(modelled using bead strings)
5 and 10 multiplication tables,
Four eggs fit in a box.
variety of
Find ¼ of 24
related division facts to perform
tables and write them
32 ÷ 2 = 16
Recognise/find/name/write fractions
18 ÷ 3 = 6
How many boxes would you need to pack 20 eggs?
24 ÷ 4 = 6
language to
written/mental calculations.
using the division and
⅓, ¼, ²⁄₄, ¾ of a (length, shape), set
Work with materials/contexts
equals signs.
of objects or quantity.
20 ÷ 2 = 10
describe
where division relate to
[Show division of two
Write simple fractions eg ½ of 6 = 3
12 ÷ 2 = 6
division.
Y2
grouping/sharing quantities.
numbers cannot be done
and recognise equivalence of two
0
3
6
9
12
15
18
in any order.]
They begin to relate these to
quarters and one half.
fractions/measures (eg 40 ÷ 2 =
Find ⅓, ¼, ²⁄₄, ¾ of a
Use commutativity/inverse relations
20, 20 is a half of 40).
length/objects/quantity.
to develop multiplicative reasoning
They connect unit fractions to
Write simple fractions
(eg 4 × 5 = 20 and 20 ÷ 5 = 4).
equal sharing and grouping, to
eg ½ of 6 = 3
numbers and to measures
Pupils develop efficient mental
Multiples of the divisor
Pupils develop reliable
Recall and use division facts for the
96 ÷ 4 = 24
Write/calculate
51 ÷ 3 =17
51 ÷ 3
3, 4 and 8 multiplication tables.
methods, using commutativity
20 x 4
4 x 4
written methods for
statements using the
= 17
85 ÷ 5 = 17
(eg 4 × 12 × 5 = 4 × 5 × 12 = 20
tables that they know
division, starting with
× 12 = 240) and multiplication
(progressing to formal
calculations of TU by U
10 x 5 = 50
Y3
and division facts (eg using 3 × 2
written methods).
7 x 5 = 35
numbers (progressing to
= 6, 6 ÷ 3 = 2 & 2 = 6 ÷ 3) to
0
80
96
TU ÷ U
formal written methods
derive related facts (30 × 2 = 60,
(divisor is 2/3/4/5/8/10)
60 ÷ 3 = 20 & 20 = 60 ÷ 3).
of short division).
Recall division facts to 12 × 12.
Practise mental methods and
Multiples of the divisor
98 ÷ 7 = 14
252 ÷ 7 = 36
252 ÷ 7 = 36
252 ÷ 7 = 36
Pupils practise to
Use place value, known/derived
extend this to HTU numbers to
become fluent in the
facts to ÷ mentally, including ÷ by 1.
derive facts, for example 200 × 3
98 ÷ 7 = 14
30 x 7 = 210
formal written method of
Find effect of dividing U/TU by
= 600 into 600 ÷ 3 = 200.
6 x 7 = 42
Y4
short division with
10/100, identifying the value of the
Relates decimal notation to
10 x 7 = 70
exact answers [NS]
digits in the answer as
4 x 7 = 28
division of whole number by 10
TU ÷ U; HTU ÷ U
units/tenths/hundredths.
and later 100.
Identify multiples/factors, including
Pupils … apply all the ÷ facts
Use the formal written
346 ÷ 8 = 43 r2 (estimate >40,
291 ÷ 3 = 97
432 ÷ 5 = 86 r2
8520 ÷ 6 = 1420
Pupils connect x by a
finding all factor pairs of a number,
0 9 7
frequently, commit them to
method of short
<50)
(estimate: 400 ÷ 5 = 80)
(estimate: 270 ÷ 3 = 90)
fraction to using fractions
& common factors of two
numbers.
memory and use them to make
division (interpret
3 2²9²1
as operators (fractions
Know/use vocabulary of prime
larger calculations.
remainders appropriately
of), and to ÷. This relates
numbers, prime factors and
for the context).
They understand the terms
composite (non-prime) nos.
to scaling by simple
factor, multiple/prime,
HTU ÷ U
Y5
Establish if a number up to 100 is
square/cube numbers & use to
fractions, incl. those > 1.
ThHTU ÷ U
prime; recall prime numbers to 19.
construct equivalent statements
Convert between units of
Find fractions of numbers
÷ nos mentally using known facts.
[eg 120 ÷15 = (30 x 4) ÷ 15 = 2 x
measure (eg km/m;
and quantities, writing
Divide whole numbers and those
4 = 8]
m/cm; cm/mm; kg/g; litre
remainders as a fraction.
involving decimals by 10/100/1000.
and ml)
Perform mental calculations,
Undertake mental calcs with
Divide numbers (up to 4
43.4 ÷ 7 = 6.2
25.6 ÷ 7 = 3.2
43.68 ÷ 7 = 6.24
496 ÷ 11
432÷ 15 = 28.8
including with mixed
increasingly large numbers and
digits) by TU whole
(estimate 42 ÷ 7 = 6)
(estimate >3, <4)
(estimate 500 ÷ 10 = 50)
(estimate: 42 ÷ 7 = 6)
operations/large numbers.
more complex calculations.
number using the formal
Identify common factors/multiples
Continue to use all table facts to
method of short/long
6
x 7 = 42
[Or compute 4368 ÷ 7,
and prime numbers.
calculate statements in order to
division (interpret as
0.2 x 7 = 1.4
then divide the solution
Use knowledge of order of
approp. for the context).
maintain their fluency.
by 100.]
operations to carry out calculations.
Y6
Use written division
Explore the order of operations
Use estimation to check answers to
methods in cases where
Adapt to own
using brackets.
calculations and determine an
Common factors can be related
the ans has up to 2dp.
appropriate degree of accuracy.
to finding equivalent fractions.
school’s
Identify value of each digit to 3dp
[Divide numbers up to
and ÷ nos by 10/100/1000 (ans to
2dp by U/TU whole
preference
3dp)
numbers.]
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4