Complex Ions Worksheet
ADVERTISEMENT
C h e m g u i d e – q u e s t i o n s
COMPLEX IONS - INTRODUCTION
1. The diagram shows the structure of a complex ion, Al(H
O)
3+
.
2
6
a) Use the diagram to explain what is meant by the term ligands.
b) What is the essential feature of a molecule or ion which can serve as a ligand?
c) What sort of bonding is there between the ligand and the metal ion?
d) What is the coordination number of the aluminium in this ion?
e) Explain what the symbols for the various bonds mean.
f) Write the electronic structure for the aluminium atom in s, p, d notation.
g) Write the electronic structure for an Al
3+
ion in s, p, d notation.
h) Explain how the aluminium ion can become attached to six water molecules.
2. Nickel forms a complex Ni(NH
)
2+
. Nickel has the electronic structure 1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
2
3p
6
3d
8
4s
2
.
3
6
Assuming that there is no rearrangement of the 3d electrons when the ammonia molecules attach to
the Ni
2+
ion, explain the bonding in the complex.
3. a) The molecule 1,2-diaminoethane is a bidentate ligand. Draw its structure.
b) Explain what is meant by a bidentate ligand, and explain why 1,2-diaminoethane can act as a
bidentate ligand.
c) Write the formula of the complex ion that this forms with Cr
3+
ions.
d) Name and draw the structure of another bidentate ligand mentioned on the Chemguide page,
making it clear in your diagram the features which enable it to act as a bidentate ligand.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1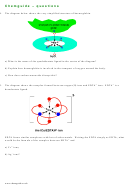 2
2