The Atypical Properties Of Beryllium Compounds
ADVERTISEMENT
C h e m g u i d e – q u e s t i o n s
GROUP 2: THE ATYPICAL PROPERTIES OF BERYLLIUM COMPOUNDS
1. This question is about beryllium chloride.
a) The other chlorides in the group are ionic solids. Explain why beryllium chloride isn't ionic.
b) Beryllium chloride boils at a much lower temperature than the other Group 2 chlorides, and in
the gas exists as a simple covalent molecule, BeCl
. This is said to be electron deficient. Draw a
2
simple dots-and-crosses diagram (outer electrons only) of BeCl
to explain what that means.
2
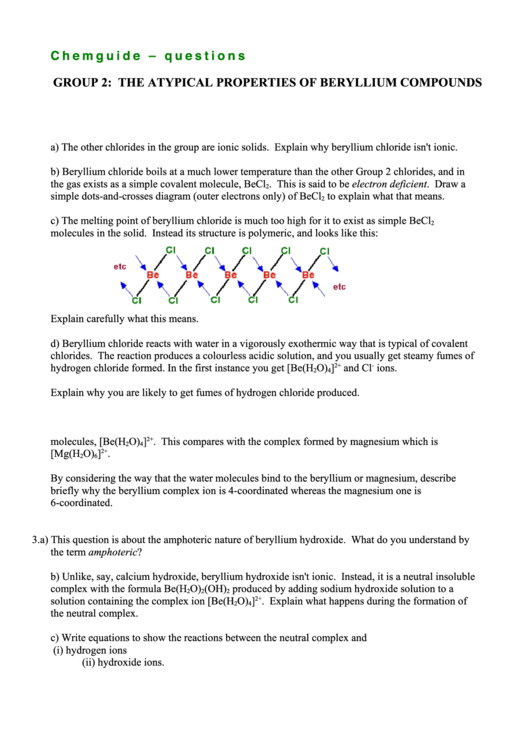
c) The melting point of beryllium chloride is much too high for it to exist as simple BeCl
2
molecules in the solid. Instead its structure is polymeric, and looks like this:
Explain carefully what this means.
d) Beryllium chloride reacts with water in a vigorously exothermic way that is typical of covalent
chlorides. The reaction produces a colourless acidic solution, and you usually get steamy fumes of
hydrogen chloride formed. In the first instance you get [Be(H
O)
]
2+
and Cl
-
ions.
2
4
Explain why you are likely to get fumes of hydrogen chloride produced.
2. This question is about the coordination number in the complex that beryllium forms with water
molecules, [Be(H
O)
]
2+
. This compares with the complex formed by magnesium which is
2
4
[Mg(H
O)
]
.
2+
2
6
By considering the way that the water molecules bind to the beryllium or magnesium, describe
briefly why the beryllium complex ion is 4-coordinated whereas the magnesium one is
6-coordinated.
3. a) This question is about the amphoteric nature of beryllium hydroxide. What do you understand by
the term amphoteric?
b) Unlike, say, calcium hydroxide, beryllium hydroxide isn't ionic. Instead, it is a neutral insoluble
complex with the formula Be(H
O)
(OH)
produced by adding sodium hydroxide solution to a
2
2
2
solution containing the complex ion [Be(H
O)
]
2+
. Explain what happens during the formation of
2
4
the neutral complex.
c) Write equations to show the reactions between the neutral complex and
(i) hydrogen ions
(ii) hydroxide ions.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1








