Mathematics Cheat Sheet For Population Biology Page 6
ADVERTISEMENT
Imaginary
(a,b) = a + bi
r
b
θ
a
Real
Figure 2: Argand diagram representing a complex number z = a + bi.
Complex Numbers We encounter complex numbers frequently when we calculate the eigen-
values of projection matrices, so it is useful to know something about them. Imaginary number:
i =
1. Complex number: z = a + bi, where a is the real part and b is a coefficient on the
imaginary part.
It is useful to represent imaginary numbers in their polar form. Define axes where the
abscissa represents the real part of a complex number and the ordinate represents the imaginary
part (these axes are known as an Argand diagram). This vector, a + bi can be represented by
the angle θ and the radius of the vector rooted at the origin to point (a, b). Using trigonometric
definitions, a = r sin θ and b = r cos θ, we see that
z = a + ib = r(cos θ + i sin θ).
Believe it or not, this comes in handy when we interpret the transient dynamics of a popu-
lation.
Let z be a complex number with real part a and imaginary part b,
z = a + bi
Then the complex conjugate of z is
¯ z = a
bi
Non-real eigenvalues of demographic projection matrices come in conjugate pairs.
3
Linear Algebra
A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers
a
a
11
12
A =
a
a
21
22
A vector is simply a list of numbers
6
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2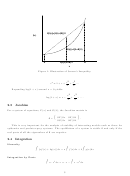 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9








