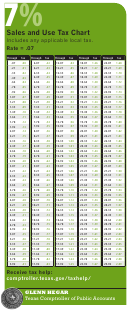
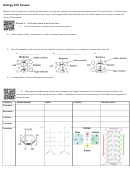
Eoc Review Part 7 Unity And Diversity Of Life, Ecological Relationships Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
What are the producers in the food web to the right?
Blossoms, Nuts, bark, leaves
What are the primary consumers?
Bees, Deer, Mice, Rabbits, Insects
What are the secondary consumers?
Bear, Wolf, Red fox, Toad, Birds
What is the highest level consumer in this
food web? Bear
What is the ultimate source of energy for
this food web? Sun
What is a food chain? Give an example of one from this food web.
A pathway that shows what organisms eat.
Blossoms → Bees → Bear
Create an energy pyramid from the food chain (label the pyramid to right) using
the following organisms: leaves → insects → birds → redfox → bear
Where is the most energy in this pyramid? Where is the least energy in this
pyramid? Most Energy: Leaves. Least Energy: Bear
What happens to the amount of energy as it moves through the food
chain/web?
Only 10% of energy at one trophic level can be used by consumers at
the next trophic level.
Assume there are 10,000 kcal of energy in the leaves. Estimate the amount of energy in each of the
other levels of the energy pyramid.
Leaves 10,000 kcal → Insects 1,000 kcal → Birds 100 kcal → Red fox 10 kcal → Bear 1 kcal
What is the role of composers in an ecosystem?
Recycle materials so they can be reused
What are the effects of bioaccumulation (biomagnification) of pesticides on a food web? At bottom of
food web the poison is at low concentration and may cause no damage. As it moves up the food web, it
builds up in the higher-level organisms and may make top level consumers sick, sterile or even dead.
Compare logistic growth and exponential growth.
Logistic: Population increases until it hits an environmental limit (lack of food, shelter) preventing
further population growth. AKA, “S Curve.”
Exponential: Population grows exponentially indefinitely.
Explain the effect of population size (think humans, introduced species, etc.) on the environment.
Not enough resources for populations that are too big; humans also generate waste and pollution;
introduced species take over (e.g., kudzu), making it difficult for native species to survive
How do increases in human populations affect populations of other organisms?
Increases in human populations can decrease other populations through hunting, habitat destruction,
pesticides
What are some examples of sustainable practices and stewardship that can protect the environment?
Answers will vary. Reduce, reuse, recycle, drive less, use alternative energy, compost, etc.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3