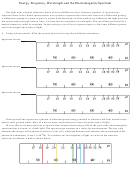
Electromagnetic Spectrum
ADVERTISEMENT
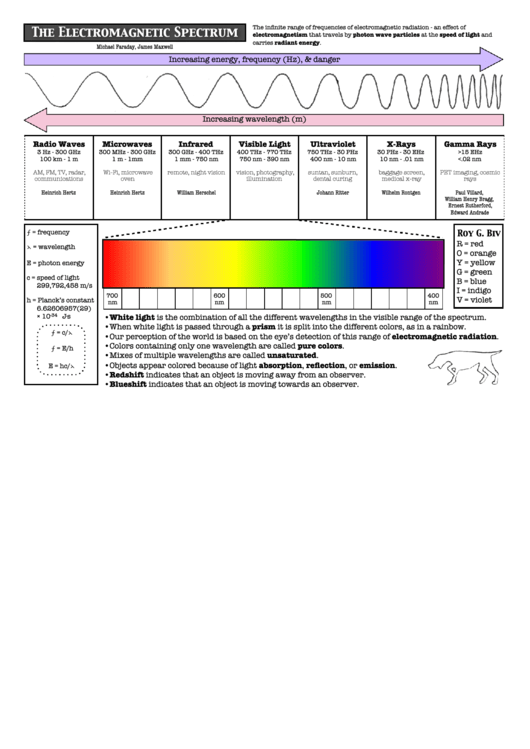
The infinite range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation - an effect of
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
electromagnetism that travels by photon wave particles at the speed of light and
carries radiant energy.
Michael Faraday, James Maxwell
Increasing energy, frequency (Hz), & danger
Increasing wavelength (m)
Radio Waves
Microwaves
Infrared
Visible Light
Ultraviolet
X-Rays
Gamma Rays
3 Hz - 300 GHz
300 MHz - 300 GHz
300 GHz - 400 THz
400 THz - 770 THz
750 THz - 30 PHz
30 PHz - 30 EHz
>15 EHz
100 km - 1 m
1 m - 1mm
1 mm - 750 nm
750 nm - 390 nm
400 nm - 10 nm
10 nm - .01 nm
<.02 nm
AM, FM, TV, radar,
Wi-Fi, microwave
remote, night vision
vision, photography,
suntan, sunburn,
baggage screen,
PET imaging, cosmic
communications
oven
illumination
dental curing
medical x-ray
rays
Heinrich Hertz
Heinrich Hertz
William Herschel
Johann Ritter
Wilhelm Rontgen
Paul Villard,
William Henry Bragg,
Ernest Rutherford,
Edward Andrade
⨍ = frequency
Roy G. Biv
R = red
⋋ = wavelength
O = orange
Y = yellow
E = photon energy
G = green
c = speed of light
B = blue
299,792,458 m/s
I = indigo
700
600
500
400
V = violet
h = Planck’s constant
nm
nm
nm
nm
6.62606957(29)
-34
•White light is the combination of all the different wavelengths in the visible range of the spectrum.
× 10
J∙s
•When white light is passed through a prism it is split into the different colors, as in a rainbow.
⨍ = c/⋋
•Our perception of the world is based on the eye’s detection of this range of electromagnetic radiation.
•Colors containing only one wavelength are called pure colors.
⨍ = E/h
•Mixes of multiple wavelengths are called unsaturated.
•Objects appear colored because of light absorption, reflection, or emission.
E = hc/⋋
•Redshift indicates that an object is moving away from an observer.
•Blueshift indicates that an object is moving towards an observer.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2