Protein Synthesis - Transcription And Translation Biology Worksheet
ADVERTISEMENT
Protein Synthesis- Transcription and Translation
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) are nucleic
acids. They are made up of smaller subunits called nucleotides.
Nucleotides are made up of three main parts: a simple sugar (deoxyribose
or D), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogen bases: adenine (A),
thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). The nucleotides in DNA
form two strands, which are held together in the center by the pairing of
nitrogen bases. Nitrogen bases always join (or pair) in the same way.
Thymine always pairs with adenine and cytosine always pairs with
guanine in DNA.
Like DNA, RNA (ribonucleic acid) contains four nitrogen bases,
but instead of thymine, RNA contains a base called uracil (U).
Unlike the double stranded DNA, RNA is made of a single strand of
nucleotides, each of which contains the simple sugar ribose (R).
Transcription
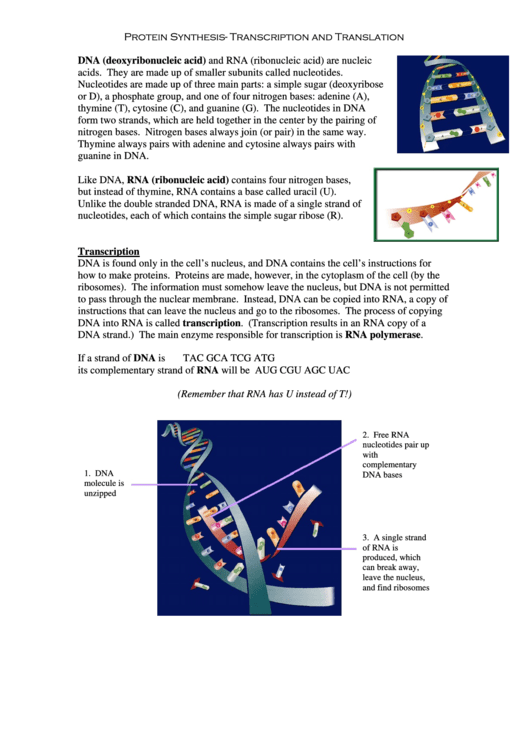
DNA is found only in the cell’s nucleus, and DNA contains the cell’s instructions for
how to make proteins. Proteins are made, however, in the cytoplasm of the cell (by the
ribosomes). The information must somehow leave the nucleus, but DNA is not permitted
to pass through the nuclear membrane. Instead, DNA can be copied into RNA, a copy of
instructions that can leave the nucleus and go to the ribosomes. The process of copying
DNA into RNA is called transcription. (Transcription results in an RNA copy of a
DNA strand.) The main enzyme responsible for transcription is RNA polymerase.
If a strand of DNA is
TAC GCA TCG ATG
its complementary strand of RNA will be
AUG CGU AGC UAC
(Remember that RNA has U instead of T!)
2. Free RNA
nucleotides pair up
with
complementary
1. DNA
DNA bases
molecule is
unzipped
3. A single strand
of RNA is
produced, which
can break away,
leave the nucleus,
and find ribosomes
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1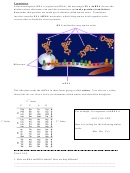 2
2 3
3