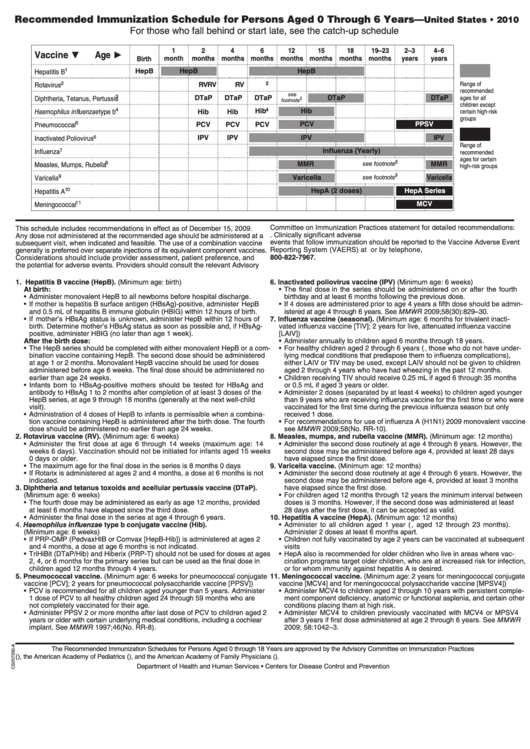
Recommended Immunization Schedule
ADVERTISEMENT
Recommended Immunization Schedule for Persons Aged 0 Through 6 Years—
United States • 2010
For those who fall behind or start late, see the catch-up schedule
1
2
4
6
12
15
18
19–23
2–3
4–6
Vaccine ▼
Age ►
Birth
month
months
months
months
months
months
months
months
years
years
HepB
HepB
HepB
1
Hepatitis B
2
RV
RV
RV
2
Range of
Rotavirus
recommended
see
DTaP
DTaP
3
DTaP
DTaP
DTaP
Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis
ages for all
3
footnote
children except
4
Hib
4
Hib
Hib
Hib
Haemophilus influenzae type b
certain high-risk
groups
5
PCV
PCV
PCV
PCV
PPSV
Pneumococcal
IPV
IPV
IPV
IPV
Inactivated Poliovirus
6
Range of
Influenza (Yearly)
7
Influenza
recommended
ages for certain
8
MMR
MMR
8
Measles, Mumps, Rubella
see footnote
high-risk groups
9
Varicella
Varicella
9
see footnote
Varicella
HepA (2 doses)
HepA Series
10
Hepatitis A
11
MCV
Meningococcal
Committee on Immunization Practices statement for detailed recommendations:
This schedule includes recommendations in effect as of December 15, 2009.
Clinically significant adverse
Any dose not administered at the recommended age should be administered at a
events that follow immunization should be reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event
subsequent visit, when indicated and feasible. The use of a combination vaccine
Reporting System (VAERS) at or by telephone,
generally is preferred over separate injections of its equivalent component vaccines.
800-822-7967.
Considerations should include provider assessment, patient preference, and
the potential for adverse events. Providers should consult the relevant Advisory
1. Hepatitis B vaccine (HepB). (Minimum age: birth)
6. Inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV) (Minimum age: 6 weeks)
At birth:
• The final dose in the series should be administered on or after the fourth
• Administer monovalent HepB to all newborns before hospital discharge.
birthday and at least 6 months following the previous dose.
• If mother is hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)-positive, administer HepB
• If 4 doses are administered prior to age 4 years a fifth dose should be admin-
and 0.5 mL of hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) within 12 hours of birth.
istered at age 4 through 6 years. See MMWR 2009;58(30):829–30.
• If mother’s HBsAg status is unknown, administer HepB within 12 hours of
7. Influenza vaccine (seasonal). (Minimum age: 6 months for trivalent inacti-
birth. Determine mother’s HBsAg status as soon as possible and, if HBsAg-
vated influenza vaccine [TIV]; 2 years for live, attenuated influenza vaccine
positive, administer HBIG (no later than age 1 week).
[LAIV])
After the birth dose:
• Administer annually to children aged 6 months through 18 years.
• The HepB series should be completed with either monovalent HepB or a com-
• For healthy children aged 2 through 6 years (i.e., those who do not have under-
bination vaccine containing HepB. The second dose should be administered
lying medical conditions that predispose them to influenza complications),
at age 1 or 2 months. Monovalent HepB vaccine should be used for doses
either LAIV or TIV may be used, except LAIV should not be given to children
administered before age 6 weeks. The final dose should be administered no
aged 2 through 4 years who have had wheezing in the past 12 months.
earlier than age 24 weeks.
• Children receiving TIV should receive 0.25 mL if aged 6 through 35 months
• Infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers should be tested for HBsAg and
or 0.5 mL if aged 3 years or older.
antibody to HBsAg 1 to 2 months after completion of at least 3 doses of the
• Administer 2 doses (separated by at least 4 weeks) to children aged younger
HepB series, at age 9 through 18 months (generally at the next well-child
than 9 years who are receiving influenza vaccine for the first time or who were
visit).
vaccinated for the first time during the previous influenza season but only
• Administration of 4 doses of HepB to infants is permissible when a combina-
received 1 dose.
tion vaccine containing HepB is administered after the birth dose. The fourth
• For recommendations for use of influenza A (H1N1) 2009 monovalent vaccine
dose should be administered no earlier than age 24 weeks.
see MMWR 2009;58(No. RR-10).
2. Rotavirus vaccine (RV). (Minimum age: 6 weeks)
8. Measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine (MMR). (Minimum age: 12 months)
• Administer the first dose at age 6 through 14 weeks (maximum age: 14
• Administer the second dose routinely at age 4 through 6 years. However, the
weeks 6 days). Vaccination should not be initiated for infants aged 15 weeks
second dose may be administered before age 4, provided at least 28 days
0 days or older.
have elapsed since the first dose.
• The maximum age for the final dose in the series is 8 months 0 days
9. Varicella vaccine. (Minimum age: 12 months)
• If Rotarix is administered at ages 2 and 4 months, a dose at 6 months is not
• Administer the second dose routinely at age 4 through 6 years. However, the
indicated.
second dose may be administered before age 4, provided at least 3 months
3. Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis vaccine (DTaP).
have elapsed since the first dose.
(Minimum age: 6 weeks)
• For children aged 12 months through 12 years the minimum interval between
• The fourth dose may be administered as early as age 12 months, provided
doses is 3 months. However, if the second dose was administered at least
at least 6 months have elapsed since the third dose.
28 days after the first dose, it can be accepted as valid.
• Administer the final dose in the series at age 4 through 6 years.
10. Hepatitis A vaccine (HepA). (Minimum age: 12 months)
4. Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine (Hib).
• Administer to all children aged 1 year (i.e., aged 12 through 23 months).
(Minimum age: 6 weeks)
Administer 2 doses at least 6 months apart.
• If PRP-OMP (PedvaxHIB or Comvax [HepB-Hib]) is administered at ages 2
• Children not fully vaccinated by age 2 years can be vaccinated at subsequent
and 4 months, a dose at age 6 months is not indicated.
visits
• TriHiBit (DTaP/Hib) and Hiberix (PRP-T) should not be used for doses at ages
• HepA also is recommended for older children who live in areas where vac-
2, 4, or 6 months for the primary series but can be used as the final dose in
cination programs target older children, who are at increased risk for infection,
children aged 12 months through 4 years.
or for whom immunity against hepatitis A is desired.
5. Pneumococcal vaccine. (Minimum age: 6 weeks for pneumococcal conjugate
11. Meningococcal vaccine. (Minimum age: 2 years for meningococcal conjugate
vaccine [PCV]; 2 years for pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine [PPSV])
vaccine [MCV4] and for meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine [MPSV4])
• PCV is recommended for all children aged younger than 5 years. Administer
• Administer MCV4 to children aged 2 through 10 years with persistent comple-
1 dose of PCV to all healthy children aged 24 through 59 months who are
ment component deficiency, anatomic or functional asplenia, and certain other
not completely vaccinated for their age.
conditions placing tham at high risk.
• Administer PPSV 2 or more months after last dose of PCV to children aged 2
• Administer MCV4 to children previously vaccinated with MCV4 or MPSV4
years or older with certain underlying medical conditions, including a cochlear
after 3 years if first dose administered at age 2 through 6 years. See MMWR
implant. See MMWR 1997;46(No. RR-8).
2009; 5 8:1042–3.
The Recommended Immunization Schedules for Persons Aged 0 through 18 Years are approved by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices
( ), the American Academy of Pediatrics ( ), and the American Academy of Family Physicians ( ).
Department of Health and Human Services • Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Medical
 1
1








