Lesson Plan National Tech-In Prevent Underage Alcohol Use Page 9
ADVERTISEMENT
Answer Key to Student Handout
6. Alcohol does not affect memory.
TRUE
FALSE
HIPPOCAMPUS—The hippocampus is the part of the brain where your memories
are made.
When alcohol reaches the hippocampus, you may have trouble
•
remembering something you just learned, such as a name or a phone
number. This can happen after just one or two drinks.
Drinking a lot of alcohol quickly can cause a blackout—not being able to
•
remember entire events, such as what you did last night.
If alcohol damages the hippocampus, you may find it hard to learn and to
•
hold on to knowledge.
7. Alcohol may make it difficult for drinkers to keep their balance or hold on to
things.
TRUE
FALSE
CEREBELLUM—The cerebellum is important for coordination, thinking, and being
aware. You may have trouble with these skills when alcohol enters the cerebellum.
After drinking alcohol, your hands may be so shaky that you can’t touch or grab
things normally. You may lose your balance and fall.
8. Under the influence of alcohol, a drinker may be emotional and weepy.
TRUE
FALSE
FRONTAL
LOBES—The brain’s frontal lobes are important for planning, forming
ideas, making decisions, and using self-control. When alcohol affects the frontal
lobes of the brain, you may find it hard to control your emotions and urges. You
may act without thinking or even become violent. Drinking alcohol over a long
period of time can damage the frontal lobes forever.
9. Alcohol will help a person sleep.
TRUE
FALSE
HYPOTHALAMUS—The hypothalamus is a small part of the brain that does an
amazing number of your body’s housekeeping chores. Alcohol upsets the work of
the hypothalamus. After a person drinks alcohol, blood pressure, hunger, thirst,
and the urge to urinate increase while body temperature and heart rate decrease.
10. Drinking alcohol will help a person lose weight.
TRUE
FALSE
HYPOTHALAMUS—The hypothalamus is a small part of the brain that does an
amazing number of your body’s housekeeping chores. Alcohol upsets the work of
the hypothalamus. After a person drinks alcohol, blood pressure, hunger, thirst,
and the urge to urinate increase while body temperature and heart rate decrease.
‐
7
‐
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10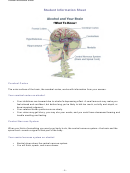 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20