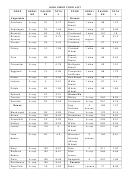
High Risk Medications List - 2017 Page 7
ADVERTISEMENT
High risk medications
U
pdated May 2017
*
Alternatives When Diagnosis is NOT KNOWN
Classification
Drug name
Risk
If diagnosis is known - refer to FER Alternatives document
pentazocine
Causes CNS adverse effects more commonly than other opioid
oxycodone/acetaminophen (generic for Percocet)
(TALACEN, TALWIN, TALWIN COMPOUND, TALWIN NX)
analgesics, including confusion and hallucinations. This drug is
tramadol (generic for Ultram)
hydromorphone
also a mixed agonist and antagonist.
oxycodone
oxymorphone
hydrocodone/acetaminophen
1
Non-COX-selective
Increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, peptic ulcer
indomethacin (INDOCIN)
acetaminophen (generic for Tylenol)
OTC
NSAIDS
disease, and acute kidney injury in older adults compared to
BEERS
ketorolac (SPRIX, TORADOL)
ibuprofen
(generic for Motrin)
other NSAID's.
BEERS
naproxen
(generic for Naprosyn)
v
diclofenac
1
Skeletal muscle
carisoprodol (SOMA)
Most muscle relaxants are poorly tolerated by older adults
acetaminophen (generic for Tylenol)
OTC
relaxants
because some have anticholinergic adverse effects, sedation,
BEERS
chlorzoxazone (LORSONE, PARAFON FORTE DSC)
ibuprofen
(generic for Motrin)
and increased risk of fractures.
BEERS
cyclobenzaprine (FLEXERIL)
naproxen
(generic for Naprosyn)
metaxalone (SKELAXIN)
diclofenac
methocarbamol (ROBAXIN)
BEERS
Use only if no heart failure and estimated GFR > 30 mL/min.
BEERS
Use PPI combination if used > 7 days.
orphenadrine (NORFLEX)
The following may also be considered, but are not recommended by
the American Geriatrics Society:
baclofen
BEERS
tizanidine
BEERS
Avoid use of tizanidine in men because of urinary retention.
References
1. Pharmacy Quality Alliance. Use of High-Risk Medications in the Elderly (HRM) . Available at: , last accessed Jan. 5, 2016.
2. American Geriatrics Society 2015 Beers Criteria Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2015 Updated Beers Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults . JAGS 2015; 1-20.
3. Hanlon JT, Semla TP, Schmader KE. Alternative Medications for Medications in the Use of High-Risk Medications in the Elderly and Potentially Harmful Drug-Disease Interactions in the Elderly Quality Measures. JAGS 2015; 1-11.
4. Clinical Pharmacology . Elsevier Gold Standard. Available at: https://
9960
* Alternatives are recommended by The American Geriatrics Society, unless otherwise noted. Alternatives are not diagnosis-specific.
¹ OTC (over-the-counter) drugs are not covered by Medicare Part D
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Medical
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7