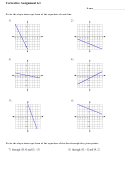
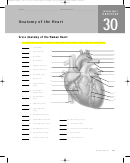
Anatomy Of The Heart Worksheet With Answers Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
ighapmLre30pg251_256 5/12/04 2:47 PM Page 254 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts:
M i c r o s c o p i c A n a t o m y o f C a r d i a c M u s c l e
Both tissue types are stri-
13. How would you distinguish the structure of cardiac muscle from the structure of skeletal muscle?
ated; thus, this is not a distinguishing feature. Skeletal muscle cells are long cylindrical cells with many nuclei per cell. Cardiac cells
have one (or two) centrally located nuclei per cell; their branched ends fit together at tight junctions called intercalated discs, which
are not seen in skeletal muscle.
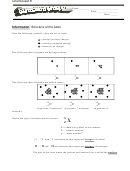
14. Add the following terms to the photo
of cardiac muscle at the right:
a.
intercalated disc
a
b. nucleus of cardiac fiber
c.
striations
d. cardiac muscle fiber
c
b
d
15. What role does the unique structure of cardiac muscle play in its function? (Note: Before attempting a response, describe the
Cardiac muscle cells form a functional syncytium by virtue of their intercalated discs. This structural feature plus
unique anatomy.)
the special arrangement of cardiac muscle in the heart allows the pumping action of the heart to be carefully coordinated for maximal
efficiency.
D i s s e c t i o n o f t h e S h e e p H e a r t
16. During the sheep heart dissection, you were asked initially to identify the right and left ventricles without cutting into the
heart. During this procedure, what differences did you observe between the two chambers?
The left ventricle was firmer, thicker, and less compressible; the right ventricle felt “flabby.”
254
Review Sheet 30
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5