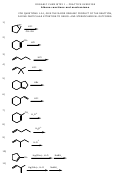
Chemical Reactions And Equations Worksheet With Answer Key - The University Of Sydney
ADVERTISEMENT
CHEM1101
2014-J-9
June 2014
Marks
• The Second Law states that all observable processes must involve a net increase in
1
entropy. When liquid water freezes into ice at 0 °C, the entropy of the water
decreases. Since the freezing of water is certainly observable, the processes must still
satisfy the Second Law. Provide a brief explanation of how this is so.
The freezing of water is exothermic and the heat evolved is passed to the
surroundings. This causes an increase in the entropy of the surroundings equal
to ΔS
= q/T where q is the heat gained by the surroundings and T is the
surroundings
temperature of the surroundings.
As long as the T is low enough, the gain in entropy in the surroundings,
ΔS
, overcomes the loss in entropy in the water, ΔS
, so that the
surroundings
system
entropy of the universe increases. Freezing is spontaneous at temperatures below
the freezing point.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40