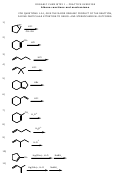
Chemical Reactions And Equations Worksheet With Answer Key - The University Of Sydney Page 3
ADVERTISEMENT
CHEM1101
2014-N-10
November 2014
1
• The Second Law states that all observable processes must involve a net increase in
entropy. When liquid water freezes into ice at 0 °C, the entropy of the water
decreases. Since the freezing of water is certainly observable, the processes must still
satisfy the Second Law. Provide a brief explanation of how this is so.
The Second Law requires that there is a net increase in the entropy of universe:
Δ
S = Δ
S + Δ
S > 0
universe
system
surroundings
When water freezes, Δ
S < 0. However, freezing is an exothermic process:
system
heat is given out to the surroundings. The heat gain in the surroundings is equal
and opposite to the heat lost in the system: q
= -Δ
H. This increases the
surr
freezing
entropy in the surroundings:
Δ
S = -Δ
H / T
surroundings
freezing
Overall:
Δ
S = Δ
S - Δ
H / T
universe
system
freezing
As long as the second term is larger than the first, Δ
S > 0. This is true at
universe
low temperatures.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40