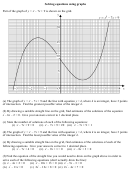
Solving Equations Examples And Worksheet
ADVERTISEMENT
A49
Appendix A.5
Solving Equations
A.5
S
E
OLVING
QUATIONS
What you should learn
Equations and Solutions of Equations
• Identify different types of equations.
An equation in is a statement that two algebraic expressions are equal. For example
x
• Solve linear equations in one variable
and equations that lead to linear
2
and
3x
5
7,
x
x
6
0,
2x
4
equations.
are equations. To solve an equation in means to find all values of for which the equa-
x
x
• Solve quadratic equations by factoring,
tion is true. Such values are solutions. For instance,
x
4
is a solution of the equation
extracting square roots, completing
the square, and using the Quadratic
3x
5
7
Formula.
because
3
4
5
7
is a true statement.
• Solve polynomial equations of
The solutions of an equation depend on the kinds of numbers being considered. For
degree three or greater.
2
instance, in the set of rational numbers,
x
10
has no solution because there is no
• Solve equations involving radicals.
rational number whose square is 10. However, in the set of real numbers, the equation
• Solve equations with absolute values.
has the two solutions
x
10
and
x
10.
• Use common formulas to solve real-
An equation that is true for every real number in the domain of the variable is called
life problems.
an identity. The domain is the set of all real numbers for which the equation is defined.
Why you should learn it
For example
Linear equations are used in many
2
x
9
x
3 x
3
Identity
real-life applications. For example, in
Exercises 155 and 156 on pages A61
is an identity because it is a true statement for any real value of x. The equation
and A62, linear equations can be used
x
1
to model the relationship between the
Identity
2
3x
3x
length of a thigh bone and the height
of a person, helping researchers learn
where
x
0,
is an identity because it is true for any nonzero real value of
x.
about ancient cultures.
An equation that is true for just some (or even none) of the real numbers in
the domain of the variable is called a conditional equation. For example, the equation
2
x
9
0
Conditional equation
is conditional because
x
3
and
x
3
are the only values in the domain that
satisfy the equation. The equation
2x
4
2x
1
is conditional because there are no
real values of for which the equation is true.
x
Linear Equations in One Variable
Definition of a Linear Equation
A linear equation in one variable is an equation that can be written in the
x
standard form
ax
b
0
where and are real numbers with a
a
b
0.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14