Covalent Molecules And Lewis Structures Worksheet With Answers Page 2
ADVERTISEMENT
Differences in electronegativities are used to predict whether the bond is nonpolar
covalent, polar covalent, or ionic. Bonds with an electronegativity difference of 0-0.4 are
considered to be nonpolar covalent. Bonds that exhibit an electronegativity difference of
more than 0.4 but less than 1.7 are classified as polar covalent. If two atoms have an
electronegativity difference of 1.7 or more, such as sodium and chloride, then one of the
atoms will lose its electron to the other atom. This results in a positively charged ion
(cation) and negatively charged ion (anion). The bond between these two ions is called an
ionic bond.
Table 1: Electronegativity and Bond Type
Table 1: Electronegativity and Bond Type
Table 1: Electronegativity and Bond Type
Electronegativity Difference
Type of Bond
Percent Ionic Character
0-0.4
nonpolar covalent bond
0-4%
Greater than 0.4 to 1.7
polar covalent bond
5-49%
Greater than or equal to 1.7
ionic bond
50-100%
Use the electronegativity values on the periodic table of the elements and the information
in Table 1 to determine the electronegativity difference, percent ionic character, and type
of bond for each formula in Table 2.
Data Table 2: Type of Bond
Data Table 2: Type of Bond
Data Table 2: Type of Bond
Data Table 2: Type of Bond
Formula
Electronegativity Difference
Type of Bond
Percent Ionic Character
KCl
3.0 - 0.8 = 2.2
ionic
50-100%
K
O
2
Br
2
MgI
2
CaCl
2
MgS
Al
S
2
3
NaCl
F
2
HCl
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5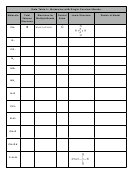 6
6 7
7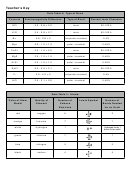 8
8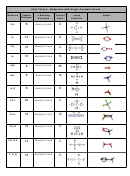 9
9 10
10