5-1 Solving Inequalities By Addition And Subtraction Worksheet With Answers Page 21
ADVERTISEMENT
5-1 Solving Inequalities by Addition and Subtraction
So, ? = 26.
Compare and contrast the graphs of a < 4 and a
In both graphs, the line is darkened to the left of 4. In the graph of a < 4, there is a circle at 4 to indicate that 4 is not
included in the graph. In the graph of a
Suppose b > d +
, c + 1 < a
4, and d +
a + 2. Order a, b, c, and d from least to greatest.
Since
, b > d.
Since
, a > c.
Since
, d > a.
So, c < a < d < b.
Write three linear inequalities that are equivalent to y < 3.
To write equivalent inequalities, add or subtract the same values from both sides of the inequality.
Sample answers: y + 1 < 2, y
1 < 4, y + 3 < 0.
Summarize the process of solving and graphing linear inequalities.
Solving linear inequalities is similar to solving linear equations. You must isolate the variable on one side of the
inequality. To graph, if the problem is a less than or a greater than inequality, an open circle is used. Otherwise a dot
is used. If the variable is on the left hand side of the inequality, and the inequality sign is less than (or less than or
equal to), the graph extends to the left; otherwise it extends to the right.
Explain why x
2 > 5 has the same solution set as x > 7.
The inequalities are equivalent. By adding 2 to each side of the first inequality, you get the second inequality.
Which equation represents the relationship shown?
x
y
1
1
2
9
3
17
4
25
5
33
6
41
y = 7x
8
y = 7x + 8
y = 8x
7
y = 8x + 7
Substitute values of x and y in the equations.
Choice A does not work for (1, 1).
Page 21
eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29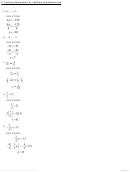 30
30 31
31








