Distance, Circles, And Quadratic Equations Worksheets Page 9
ADVERTISEMENT
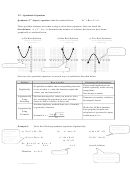
Appendix H: Distance, Circles, and Quadratic Equations
H9
50. Find an equation of the line that is tangent to the circle at
73. Graph
√
√
(a) y =
x + 5
(b) x = −
4 − y.
the point P on the circle
+ y
+ 2x = 9; P (2, −1)
2
2
(a) x
74. Graph
√
√
+ y
− 6x + 4y = 13; P (4, 3).
2
2
(b) x
(a) y = 1 +
4 − x
(b) x = 3 +
y.
+ y
= 20 and the point P (−1, 2):
2
2
51. For the circle x
75. If a ball is thrown straight up with an initial velocity of
(a) Is P inside, outside, or on the circle?
32 ft / s, then after t seconds the distance s above its starting
(b) Find the largest and smallest distances between P and
height, in feet, is given by s = 32t − 16t
2
.
points on the circle.
(a) Graph this equation in a ts-coordinate system (t-axis
52. Follow the directions of Exercise 51 for the circle
horizontal).
+ y
− 2y − 4 = 0
2
2
(b) At what time t will the ball be at its highest point, and
x
how high will it rise?
5
and the point P 3,
.
2
76. A rectangular field is to be enclosed with 500 ft of fencing
53. Referring to the accompanying figure, find the coordinates
along three sides and by a straight stream on the fourth side.
of the points T and T , where the lines L and L are tangent
Let x be the length of each side perpendicular to the stream,
to the circle of radius 1 with center at the origin.
and let y be the length of the side parallel to the stream.
L
y
(a) Express y in terms of x.
T
(b) Express the area A of the field in terms of x.
(c) What is the largest area that can be enclosed?
x
77. A rectangular plot of land is to be enclosed using two kinds
1
(3, 0)
of fencing. Two opposite sides will have heavy-duty fenc-
ing costing $3 / ft, and the other two sides will have standard
T ′
fencing costing $2 / ft. A total of $600 is available for the
L′
Figure Ex-53
fencing. Let x be the length of each side with the heavy-
√
duty fencing, and let y be the length of each side with the
54. A point (x, y) moves so that its distance to (2, 0) is
2 times
standard fencing.
its distance to (0, 1).
(a) Express y in terms of x.
(a) Show that the point moves along a circle.
(b) Find a formula for the area A of the rectangular plot in
(b) Find the center and radius.
terms of x.
55. A point (x, y) moves so that the sum of the squares of its
(c) What is the largest area that can be enclosed?
distances from (4, 1) and (2, −5) is 45.
78. (a) By completing the square, show that the quadratic equa-
(a) Show that the point moves along a circle.
tion y = ax
+ bx + c can be rewritten as
2
(b) Find the center and radius.
56. Find all values of c for which the system of equations
2
2
b
b
y = a x +
+ c −
− y
= 0
2
2
x
2a
4a
(x − c)
+ y
= 1
2
2
if a = 0.
has 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4 solutions. [Hint: Sketch a graph.]
(b) Use the result in part (a) to show that the graph of the
quadratic equation y = ax
+ bx + c has its high point
2
57–70
Graph the parabola and label the coordinates of the ver-
at x = −b / (2a) if a < 0 and its low point there if a > 0.
I
tex and the intersections with the coordinate axes.
57. y = x
+ 2
58. y = x
− 3
2
2
79–80
I
Solve the given inequality.
59. y = x
+ 2x − 3
60. y = x
− 3x − 4
2
2
+ 5x − 1 < 0
− 2x + 3 > 0
2
2
79. (a) 2x
(b) x
61. y = −x
+ 4x + 5
62. y = −x
+ x
2
2
+ x − 1 > 0
− 4x + 6 < 0
2
2
80. (a) x
(b) x
63. y = (x − 2)
64. y = (3 + x)
2
2
81. At time t = 0 a ball is thrown straight up from a height of
− 2x + y = 0
+ 8x + 8y = 0
2
2
65. x
66. x
5 ft above the ground. After t seconds its distance s, in feet,
67. y = 3x
− 2x + 1
68. y = x
+ x + 2
2
2
above the ground is given by s = 5 + 40t − 16t
2
.
69. x = −y
+ 2y + 2
70. x = y
− 4y + 5
2
2
(a) Find the maximum height of the ball above the ground.
(b) Find, to the nearest tenth of a second, the time when the
71. Find an equation of
ball strikes the ground.
(a) the right half of the parabola y = 3 − x
2
(c) Find, to the nearest tenth of a second, how long the ball
(b) the left half of the parabola y = x
− 2x.
2
will be more than 12 ft above the ground.
72. Find an equation of
82. Find all values of x at which points on the parabola y = x
2
(a) the upper half of the parabola x = y
− 5
2
lie below the line y = x + 3.
(b) the lower half of the parabola x = y
− y − 2.
2
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9