Physics 40 Hw #11 Worksheet With Answers
ADVERTISEMENT
Physics 40 HW #11 Key
Ch10: 25, 27, 43
Ch 11: 1,3, 5, 7, 9, 13, 15, 17, 19, 25, 31, 37, 41
10.25.
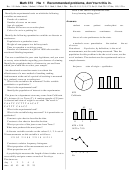
Model: For an energy diagram, the sum of the kinetic and potential energy is a constant.
Visualize:
x
That is,
K at
x
Since the
The particle is released from rest at
1 0 m
0
1 0 m
total energy is given by
E K U
,
we can draw a horizontal total energy (TE) line
x
through the point of intersection of the potential energy curve (PE) and the
1 0 m
line. The distance from the PE curve to the TE line is the particle’s kinetic energy.
These values are transformed as the position changes, causing the particle to speed up
or slow down, but the sum K U
does not change.
E
Solve: (a) We have
4 0 J
and this energy is a constant. For
x
1 0,
U
4 0 J
and,
therefore,
K
must
be
negative
to
keep
E
the
same
Since negative kinetic energy is unphysical,
(note that
K
E U
or
K
4 0 J
U
)
the particle cannot move to the left. That is, the particle will move to the right of
x
1 0 m
This means the particle has maximum speed or maximum kinetic energy
(b) The expression for the kinetic energy is E U
x
Thus,
when U is minimum. This happens at
4 0 m
1
2(3 0 J)
8 0 J
2
K
E U
(4 0 J) (1 0 J) 3 0 J
mv
3 0 J
v
17 3 m/s
max
min
max
max
2
m
0 020 kg
x
4 0 m
The particle possesses this speed at
x
x
These are the turning
(c) The total energy (TE) line intersects the potential energy (PE) curve at
1 0 m
and
6 0 m
points of the motion.
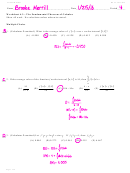
10.27.
Model: For an energy diagram, the sum of the kinetic and potential energy is a constant.
Visualize:
For the speed of the particle at A that is needed to reach B to be a minimum, the particle’s kinetic energy as it reaches the top
must be zero. Similarly, the minimum speed at B for the particle to reach A obtains when the particle just makes it to the top
with zero kinetic energy.
Solve: (a) The energy equation
K
U
K
U
is
A
A
top
top
1
2
mv
U
0 J
U
A
A
top
2
v
2(
U
U
)/
m
2(5.0 J 2.0 J)/0.100 kg
7.7 m/s
A
top
A
(b) To go from point B to point A,
K
U
K
U
is
B
B
top
top
1
2
mv
U
0 J
U
B
B
top
2
v
2(
U
U
)/
m
2(5 0 J 0 J)/0 100 kg 10 0 m/s
B
top
B
Assess: The particle requires a higher kinetic energy to reach A from B than to reach B from A.
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6