Electron Configurations Worksheet Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
7. Consider the orbital diagram for oxygen in Model 2.
a. How many electrons are present in the orbital diagram?
b. Based on its position in the periodic table, explain how you know that your answer to part a
is the correct number of electrons for oxygen.
8. Examine the orbital diagrams and electron configurations in Model 2. Using the following elec-
tron configuration:
1 s
2
2 s
2
2 p
4
a. Underline the energy levels.
b. Circle the sublevels.
c. Draw a box around the numbers of electrons.
9. The 2s and 2p sublevels are very close in energy, as are the 3s and 3p sublevels. Explain how the
orbital diagram for sodium confirms that the 3s sublevel is lower in energy than the 3p sublevel.
10. The lowest potential energy arrangement of electrons in an atom is called the ground state.
Ground state electron configurations can be predicted by a strict set of rules known as the
Aufbau principle (“aufbau”means filling up). Examine the diagrams in Model 2 and the state-
ments below to determine the phrase that best describes each rule. Circle the correct answer.
a. Based on where a single electron is placed, the lowest potential energy electron in an atom is
found in the ________ sublevel.
1s
2s
3s
b. Electrons will occupy a p-orbital only after ____________ .
the previous s-orbital is half full
the previous s-orbital is completely full
the previous s-orbital is empty
c. Electrons can begin to occupy energy levels with the next highest integer designation (e.g.,
2 vs. 1, 3 vs. 2) only after __________________ on the energy level below it are occupied.
half of the orbitals
at least one of the orbitals
all of the orbitals
4
POGIL
Activities for High School Chemistry
™
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2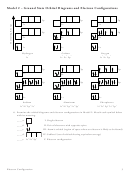 3
3 4
4 5
5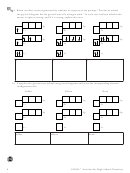 6
6 7
7 8
8