Chemical Bonding Worksheets
ADVERTISEMENT
CHAPTER 10: CHEMICAL BONDING
Problems: 1-11, 13-52, 55-58, 61-64, 65a-c, 66(c,d), 67-68, 69b-d, 71, 75-80, 83-90, 91(b,d), 92(c,d), 95-96, 99, 101
10.1 BONDING MODELS AND AIDS DRUGS
An American chemist named Gilbert N. Lewis developed the Lewis bonding theory in which
electrons are represented as dots.
→ The molecules represented are called Lewis structures or Lewis electron-dot formulas.
Today we use Lewis structures to determine how
atoms are arranged in a molecule and to predict the
3D shape of molecules.
→ Knowing the shape of a molecule allows us to
explain the observed properties and behavior of
these substances.
– For example, we can use the structure of the
caffeine molecule to explain how the
molecule acts as a stimulant.
ball-and-stick model of a caffeine molecule
10.2 REPRESENTING VALENCE ELECTRONS WITH DOTS
TYPES OF CHEMICAL BONDS
chemical bond: what holds atoms or ions together in a compound
The two types of chemical bonds are ionic bonds and covalent bonds.
– Ionic bonds hold ions together in ionic compounds.
– Covalent bonds hold atoms together in molecules.
10.3 LEWIS STRUCTURES OF IONIC COMPOUNDS: Electrons Transferred
Metals lose electrons from their valence shell
→ positively charged ions = cations
Nonmetals gain electrons, adding electrons to their valence shell.
→ negatively charged ions = anions
Elements tends to gain or lose electrons, so they will have the same number of electrons
as a Noble gas to become more stable.
→ Ions formed by main-group elements are usually isoelectronic with—i.e., have the
same number of electrons as—one of the noble gases!
CHEM 121 Tro Chapter 10 F2012
page 1 of 22
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14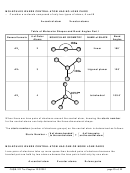 15
15 16
16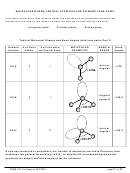 17
17 18
18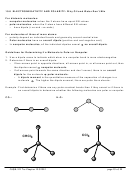 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22








