Similar Triangles, Right Triangles, And The Definition Of The Sine, Cosine And Tangent Functions Of Angles Of A Right Triangle Worksheets With Answer Key Page 32
ADVERTISEMENT
θ
2
tan
=
175. _______________________
θ
−
2
1
tan
The half-angle, double-angle, and sum and difference identities can be used to evaluate the
trigonometric functions for certain special angles. The following examples illustrate this use.
Example: Evaluate sin 75°
Solution: Since 75° = 30° + 45°, we have
sin 75° = sin (30° + 45°) = sin 30° cos 45° + cos 30° sin 45°
+
1
2
3
2
2
6
=
⋅
+
⋅
=
2
2
2
2
4
π
Example: Evaluate
cos
.
8
π
π
1
=
Solution: Apply the half-angle identity for the cosine to the angle
.
8
2
4
π
+
+
2
1
cos
π
π
1
1
1
4
2
=
=
=
=
+
cos
cos
2
. 2
8
2
4
2
2
2
π
Notice that the + sign is chosen for the radical because
is a quadrant I angle and the
8
cosine is positive in quadrant I.
8
Example: Find sin 2θ, if sin θ
=
−
and θ is a quadrant IV angle.
17
Solution: By the double-angle identity,
θ
θ
θ
sin 2
= 2 sin
cos
.
8
θ
θ
=
−
Since sin
, the missing piece in this puzzle is the value of cos
. Since
17
θ
θ
2
2
sin
+ cos
= 1, we have
2
8
θ
−
+
=
2
cos
1
17
so that
64
225
θ
=
−
=
2
cos
1
289
289
and hence,
15
θ
=
±
cos
.
17
θ
We must choose the + sign because
is a quadrant IV angle and the cosine is positive
in quadrant IV. Thus,
- 32 -
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2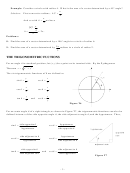 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43