Quadratic Equations Worksheet Page 4
ADVERTISEMENT
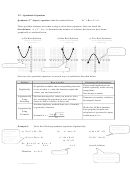
Solution Using the Quadratic Formula
Factoring is useful only for those quadratic equations which have whole numbers. When you encounter
quadratic equations that can not be easily factored out, use the quadratic formula to find the value of x:
− ±
−
2
b
b
4
ac
=
x
2
a
− = −
2
Examples:
x
8
2
x
+
− =
← Rewrite in standard form, where
=
=
= −
2
x
2
x
8 0
a
1
, b
2 and
,
c
8
− ±
−
−
2
4 4 1
( )(
8
)
x =
← Plug in numbers into the equation
2 1
( )
− ±
2
36
=
2 1
( )
− ±
2 6
=
2
=
−
← The two rational solutions
2 4
,
−
+ =
2
3
x
13
x
4 0
− −
±
−
−
2
(
13
)
(
13
)
4 3 4
( )( )
x =
2 3
( )
±
13
121
=
6
±
13
11
=
6
24
2
1
= 4
=
← The two rational solutions
,
,
6
6
3
In some cases you encounter repeated rational solutions. And to prove you have the right values you use
the discriminant which gives you information about the nature of the solutions to the equation. Based on
−
2
the expression b
4
ac
, which is under the radical in the quadratic formula it can be found in the
+
+ = .
2
equation ax
bx c
0
I. When the discriminant is equal to 0, the equation has repeated rational solutions.
−
+ =
2
Example:
x
2
x
1 0
−
= −
−
=
2
2
By using the discriminant b
4
ac
(
2
)
4 1 1
( )( )
0
− −
±
−
−
2
(
2
)
(
2
)
4 1 1
( )( )
x =
2 1
( )
±
2
0
=
2
=
← Repeated rational solutions
x
1 1
,
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12