Chapter 9 Probability Worksheet Page 15
ADVERTISEMENT
The Fundamental Counting Principle can be used to find the number of
possible outcomes and solve probability problems in more complex
problems, when there are more than two events.
2
JEANS
The Jean Shop sells
The Jeans Shop
young men’s jeans in different
Waist Size
Length (in.)
Style
sizes, styles, and lengths, as
shown in the table. Find the
number of jeans available.
Then find the probability of
30
30
slim fit
selecting a size 32 × 34 slim fit.
32
32
bootcut
34
34
loose fit
36
38
sizes
style
length
total
Fundamental
3
5
3
45
·
·
=
Counting Principle
There are 45 different types of jeans to choose from. Out of the 45
possible outcomes, only one is favorable. So, the probability of
_
1
randomly selecting a 32 × 34 slim fit is
Jean size
Jean size
.
45
In mens’ jeans, the size is
labeled waist × length.
So, a 32 × 34 is a
32-inch waist with a
34-inch length.
JEANS
If the Jean Shop adds relaxed fit jeans to its selection, find
b.
the number of available jeans. Then find the probability of
randomly selecting a 36 × 30 relaxed fit pair of jeans.
Example 1
Use the Fundamental Counting Principle to find the
(p. 471)
total number of outcomes in each situation.
tossing a quarter, a dime, and a nickel
1.
choosing scrambled, sunny-side up, or poached
2.
eggs with bacon or sausage and milk or orange juice
choosing a number on a number cube and picking
3.
a marble from the bag at the right
4 3
Example 2
CLOTHES
Beth has 3 sweaters, 4 blouses, and 6 skirts
4.
(p. 472)
that coordinate. Find the number of different outfits
consisting of a sweater, blouse, and skirt that are possible.
Then find the probability of randomly selecting a particular
sweater-blouse-skirt outfit.
472
Chapter 9 Probability
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5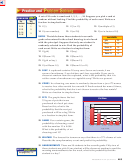 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48








