Shapes, And Bond Angles Of Molecules Worksheet Page 11
ADVERTISEMENT
3 bonding pairs of electrons & 0 lone pairs of
H
CO
electrons around the central carbon atom.
2
Trigonal
Trigonal
methanal
3
120º
Bonding pairs of electrons repel each other
Polar
planar
planar
equally. OR 3 negative charge centers
arranged as far apart as possible.
2 bonding pairs & 1 lone pair of electrons
SO
Trigonal
around the central sulfur atom. Lone pair -
2
3
~117º
bent
Polar
Sulfur dioxide
planar
bonding pair repulsion is greater than
bonding pair – bonding pair repulsion.
3 bonding pairs & 0 lone pairs of electrons
around each carbon atom. 3 bonding pairs
120º
3 for
Trigonal
of electrons repel each other equally in order
C
H
between
Trigonal
Non
2
4
each C
planar for
to minimize the repulsion.
OR
ethene
each H
planar
Polar
atom
each C atom
3 negative charge centers on each carbon
atom
atom arranged as far apart as possible to
minimize repulsion.
4 bonding pairs & 0 lone pairs of electrons
Non
CH
around the central carbon atom. In order to
4
4
Tetrahedral
109.5º
Tetrahedral
Polar
methane
minimize the repulsions the 4 bonding pairs
of electrons repel each other equally.
4 bonding pairs & 0 lone pairs of electrons
Non
SiCl
4
Tetrahedral
109.5º
Tetrahedral
around the central silicon atom. 4 bonding
4
Polar
pairs of electrons repel each other equally.
4 bonding pairs & 0 lone pairs of electrons
CClF
4
Tetrahedral
109.5º
Tetrahedral
around the central chlorine atom. 4 bonding
Polar
3
pairs of electrons repel each other equally.
2 bonding pairs of electrons and 2 lone pairs
of electrons around the central oxygen atom.
H
O
4
Tetrahedral
104.5º
Bent
The 2 lone pairs of electrons exert a greater
Polar
2
repulsion than the bonding pair and lone-
bonding pair repulsion.
11
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10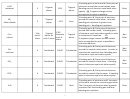 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14








