Propositional Logic Worksheet Page 18
ADVERTISEMENT
Examples with Identities
1. P ≡ P ∧ P - idempotence of ∧
“Anna is wretched” is equivalent to “Anna is wretched and Anna is
wretched”.
2. P ≡ P ∨ P - idempotence of ∨
“Anna is wretched” is equivalent to “Anna is wretched or wretched”.
3. P ∨ Q ≡ Q ∨ P - commutativity
“Sam is rich or happy” is equivalent to “Sam is happy or rich”.
′
3
. P ∧ Q ≡ Q ∧ P
“Sam is rich and Sam is happy” is equivalent to “Sam is happy and
Sam is rich”.
4. ¬(P ∨ Q) ≡ ¬P ∧ ¬Q - DeMorgan’s law
“It is not the case that Sam is rich or happy” is equivalent to “Sam
is not rich and he is not happy”.
′
4
. ¬(P ∧ Q) ≡ ¬P ∨ ¬Q
“It is not true that Abby is quick and strong” is equivalent to “Abby
is not quick or Abby is not strong”.
5. P ∧ (Q ∨ R) ≡ (P ∧ Q) ∨ (P ∧ R) - distributivity
“Abby is strong, and Abby is happy or nervous” is equivalent to
“Abby is strong and happy, or Abby is strong and nervous”.
′
5
. P ∨ (Q ∧ R) ≡ (P ∨ Q) ∧ (P ∨ R)
“Sam is tired, or Sam is happy and rested” is equivalent to “Sam is
tired or happy, and Sam is tired or rested”.
6. P ∨ ¬P ≡ T - negation law
“Ted is healthy or Ted is not healthy” is true.
′
6
. P ∧ ¬P ≡ F
“Kate won the lottery and Kate didn’t win the lottery” is false.
18
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16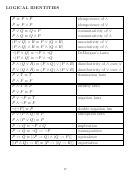 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21








