Propositional Logic Worksheet Page 19
ADVERTISEMENT
7. ¬(¬P ) ≡ P - double negation
“It is not the case that Tom is not rich” is equivalent to “Tom is
rich”.
8. P ∨ (P ∧ Q) ≡ P - absorption
“Kate is happy, or Kate is happy and healthy” is true if and only if
“Kate is happy” is true.
′
8
. P ∧ (P ∨ Q) ≡ P
“Kate is sick, and Kate is sick or angry” is true if and only if “Kate
is sick” is true.
9. P → Q ≡ ¬P ∨ Q - implication
“If I win tne lottery, then I will give you half the money” is true
exactly when I either don’t win the lottery, or I give you half the
money.
10. P → Q ≡ ¬Q → ¬P - contrapositive
“If Anna is healthy, then she is happy” is equivalent to “If Anna is
not happy, then she is not healthy”.
11. P ↔ Q ≡ (P → Q) ∧ (Q → P ) equivalence
“Anna is healthy if and only if she is happy” is equivalent to “If
Anna is healthy, then she is happy, and if Anna is happy, then she is
healthy”.
12. (P ∧ Q) → R ≡ P → (Q → R) - exportation
“Anna is famous implies that if she is rich, then she is happy” is
equivalent to “If Anna is famous and rich, then she is happy”.
19
ADVERTISEMENT
0 votes
Related Articles
Related forms
Related Categories
Parent category: Education
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16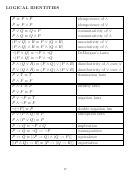 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21








